OPTN/SRTR 2016 Annual Data Report: Kidney
- PMID: 29292608
- PMCID: PMC5772947
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14557
OPTN/SRTR 2016 Annual Data Report: Kidney
Abstract
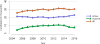
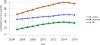
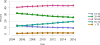
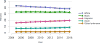
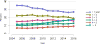
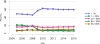
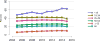
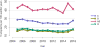
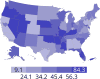
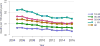
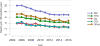
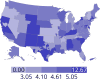
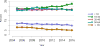
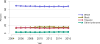
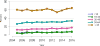
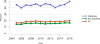
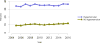
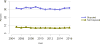
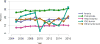
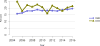
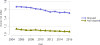
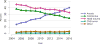
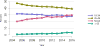
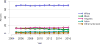
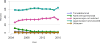
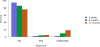
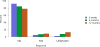
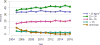
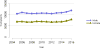
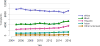
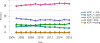
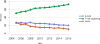
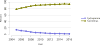
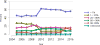
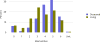
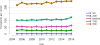
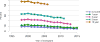
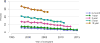
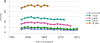
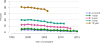
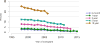
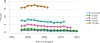
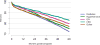
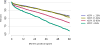
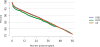
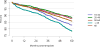
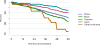
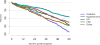
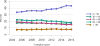
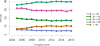
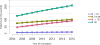
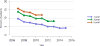
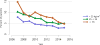
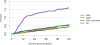
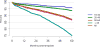
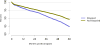
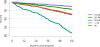
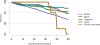
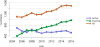
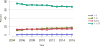
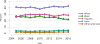
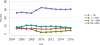
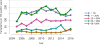
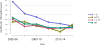
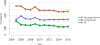
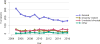
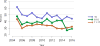
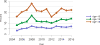
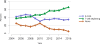
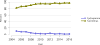
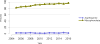
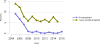
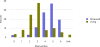
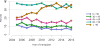
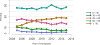
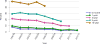
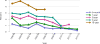
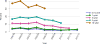
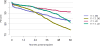
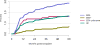
Data from 2016 show ongoing positive trends in short- and long-term allograft survival, and a decrease in the number of active listed candi- dates for the first time in more than a decade, with a concomitant in- crease in deceased donor kidney transplants. Transplant rates that had changed dramatically for some groups after implementation of the new kidney allocation system in 2014 are stabilizing, allowing for evaluation of new steady states and trends. Many challenges remain in adult kid- ney transplantation, including stagnant rates of living donor transplant, geographic disparities in access to transplant, racial disparities in living donor transplant, and overall a continuing demand for kidneys that far outpaces the supply. For pediatric recipients, a decline in the proportion of living donor transplants is of concern. In 2016, only 34.2% of pediatric transplants were from living donors, compared with 47.2% in 2005. The number of related donors decreased dramatically over the past decade, and the number of unrelated directed transplants performed in pediatric candidates remained low (50).
.
Figures














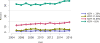













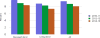







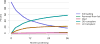







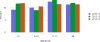

Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

