Electrifying Organic Synthesis
- PMID: 29292849
- PMCID: PMC5969240
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201711060
Electrifying Organic Synthesis
Abstract
The direct synthetic organic use of electricity is currently experiencing a renaissance. More synthetically oriented laboratories working in this area are exploiting both novel and more traditional concepts, paving the way to broader applications of this niche technology. As only electrons serve as reagents, the generation of reagent waste is efficiently avoided. Moreover, stoichiometric reagents can be regenerated and allow a transformation to be conducted in an electrocatalytic fashion. However, the application of electroorganic transformations is more than minimizing the waste footprint, it rather gives rise to inherently safe processes, reduces the number of steps of many syntheses, allows for milder reaction conditions, provides alternative means to access desired structural entities, and creates intellectual property (IP) space. When the electricity originates from renewable resources, this surplus might be directly employed as a terminal oxidizing or reducing agent, providing an ultra-sustainable and therefore highly attractive technique. This Review surveys recent developments in electrochemical synthesis that will influence the future of this area.
Keywords: electrochemistry; oxidation; reduction; sustainable chemistry; synthetic methods.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures



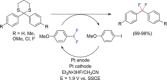
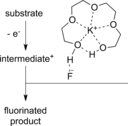



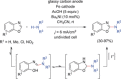
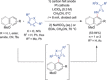











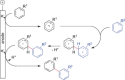
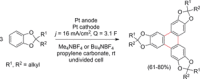
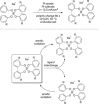
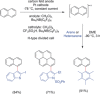












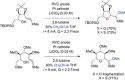



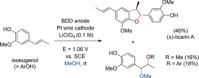
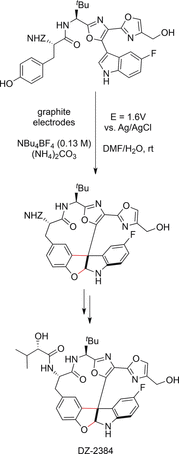

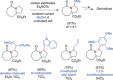
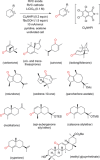
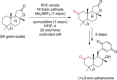
References
-
- J. G. J. Olivier, G. Janssens-Maenhout, M. Muntean, J. A. H. W. Peters, Trends in Global CO2 Emissions: 2016 Report, The Hague, 2016.
-
- Renewables 2017: Global Status Report, REN21, Paris, 2017.
-
- Jörissen J., Speiser B., Preparative Electrolysis on the Laboratory Scale, 5th ed. (Eds.: O. Hammerich, B. Speiser), CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2016, pp. 263–330.
-
- None
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

