Identification and evaluation of reference genes for qRT-PCR studies in Lentinula edodes
- PMID: 29293626
- PMCID: PMC5749753
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190226
Identification and evaluation of reference genes for qRT-PCR studies in Lentinula edodes
Abstract
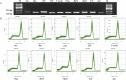
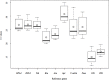
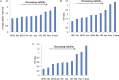
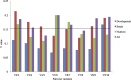
Lentinula edodes (shiitake mushroom) is a common edible mushroom with a number of potential therapeutic and nutritional applications. It contains various medically important molecules, such as polysaccharides, terpenoids, sterols, and lipids, were contained in this mushroom. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) is a powerful tool to analyze the mechanisms underlying the biosynthetic pathways of these substances. qRT-PCR is used for accurate analyses of transcript levels owing to its rapidity, sensitivity, and reliability. However, its accuracy and reliability for the quantification of transcripts rely on the expression stability of the reference genes used for data normalization. To ensure the reliability of gene expression analyses using qRT-PCR in L. edodes molecular biology research, it is necessary to systematically evaluate reference genes. In the current study, ten potential reference genes were selected from L. edodes genomic data and their expression levels were measured by qRT-PCR using various samples. The expression stability of each candidate gene was analyzed by three commonly used software packages: geNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper. Base on the results, Rpl4 was the most stable reference gene across all experimental conditions, and Atu was the most stable gene among strains. 18S was found to be the best reference gene for different development stages, and Rpl4 was the most stably expressed gene under various nutrient conditions. The present work will contribute to qRT-PCR studies in L. edodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sugui M, De Lima PA, Delmanto R, Da Eira A, Salvadori DMF, Ribeiro LR. Antimutagenic effect of Lentinula edodes (BERK.) Pegler mushroom and possible variation among lineages. Food and chemical toxicology. 2003; 41: 555–560. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(02)00306-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jiang T, Luo S, Chen Q, Shen L, Ying T. Effect of integrated application of gamma irradiation and modified atmosphere packaging on physicochemical and microbiological properties of shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes). Food Chemistry. 2010;122: 761–767. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.050 - DOI
-
- Kupfahl C, Geginat G, Hof H. Lentinan has a stimulatory effect on innate and adaptive immunity against murine Listeria monocytogenes infection. International immunopharmacology. 2006; 6: 686–696. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2005.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M, Takatsuki F, Maeda YY, Hamuro J, Chihara G. Antitumor and immunological activity of lentinan in comparison with LPS. International Journal of Immunopharmacology.1994; 16: 463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/0192-0561(94)90037-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maruyama S, Sukekawa Y, Kaneko Y, Fujimoto S. Anti tumor activities of lentinan and micellapist in tumor-bearing mice. Gan to kagaku ryoho Cancer & chemotherapy. 2006; 33: 1726–1729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

