Influence of Botanical Origin and Chemical Composition on the Protective Effect against Oxidative Damage and the Capacity to Reduce In Vitro Bacterial Biofilms of Monofloral Honeys from the Andean Region of Ecuador
- PMID: 29295525
- PMCID: PMC5795995
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19010045
Influence of Botanical Origin and Chemical Composition on the Protective Effect against Oxidative Damage and the Capacity to Reduce In Vitro Bacterial Biofilms of Monofloral Honeys from the Andean Region of Ecuador
Abstract
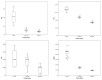
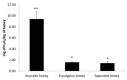
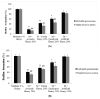
Three types of monofloral honey from the Andean regions of Ecuador (Avocado, Eucalyptus, and Rapeseed honey) were analyzed to determine their floral origin, physicochemical parameters, chemical composition, antioxidant capacity, and their capacity to reduce in vitro bacterial biofilms. The chemical composition varied considerably depending on floral origin. The highest values of bioactive compounds were found in Avocado honey, classified as dark amber in color, while the lowest values were found in Eucalyptus honey followed by Rapeseed honey, both classified as extra light amber. When compared to Eucalyptus and Rapeseed honey, Avocado honey showed a more effective superoxide scavenging activity, chelating metal ions capacity, and a higher ability to protect human erythrocyte membranes against lipid peroxidation. For antimicrobial activity, the hydrogen peroxide content and the capacity to inhibit the biofilm formation, and to remove preformed biofilm from Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae was determined. Avocado honey showed the highest values of hydrogen peroxide content, as well as the highest capacity to reduce in vitro bacterial biofilms. A correlation between color vs. phenolics content vs. superoxide scavenging activity vs. chelating metal ions capacity, and the capacity to protect human erythrocyte membranes against lipid peroxidation was found.
Keywords: Ecuadorian monofloral honey; Eucalyptus honey; Rapeseed honey; avocado honey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez-Suarez J.M., Giampieri F., Cordero M., Gasparrini M., Forbes-Hernandez T.Y., Mazzoni L., Afrin S., Beltrán-Ayala P., Gonzales-Paramas A.M., Santos-Buelga C., et al. Activation of AMPK/Nrf2 signalling by Manuka honey protects human dermal fibroblasts against oxidative damage by improving antioxidant response and mitochondrial function promoting wound healing. J. Funct. Foods. 2016;25:38–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.05.008. - DOI
-
- Scepankova H., Saraiva J.A., Estevinho L.M. Honey Health Benefits and Uses in Medicine. In: Alvarez-Suarez J.M., editor. Bee Products—Chemical and Biological Properties. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. pp. 83–96.
-
- Santos-Buelga C., González-Paramás A.M. Chemical Composition of Honey. In: Alvarez-Suarez J.M., editor. Bee Products—Chemical and Biological Properties. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. pp. 43–82.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

