Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 29295587
- PMCID: PMC5943940
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23010040
Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
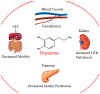
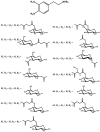
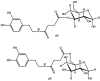
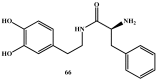
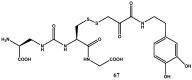
Background: Parkinson's disease is an aggressive and progressive neurodegenerative disorder that depletes dopamine (DA) in the central nervous system. Dopamine replacement therapy, mainly through actual dopamine and its original prodrug l-dopa (LD), faces many challenges such as poor blood brain barrier penetration and decreased response to therapy with time. Methods: The prodrugs described herein are ester, amide, dimeric amide, carrier-mediated, peptide transport-mediated, cyclic, chemical delivery systems and enzyme-models prodrugs designed and made by chemical means, and their bioavailability was studied in animals. Results: A promising ester prodrug for intranasal delivery has been developed. LD methyl ester is currently in Phase III clinical trials. A series of amide prodrugs were synthesized with better stability than ester prodrugs. Both amide and dimeric amide prodrugs offer enhanced blood brain barrier (BBB) penetration and better pharmacokinetics. Attaching LD to sugars has been used to exploit glucose transport mechanisms into the brain. Conclusions: Till now, no DA prodrug has reached the pharmaceutical market, nevertheless, the future of utilizing prodrugs for the treatment of PD seems to be bright. For instance, LD ester prodrugs have demonstrated an adequate intranasal delivery of LD, thus enabling the absorption of therapeutic agents to the brain. Most of the amide, cyclic, peptidyl or chemical delivery systems of DA prodrugs demonstrated enhanced pharmacokinetic properties.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; blood brain barrier; dopamine; levodopa; prodrug.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this review have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
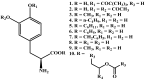
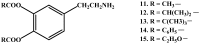

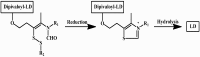
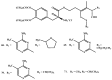
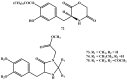
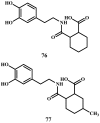
Similar articles
-
Designing prodrugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012 May;7(5):385-406. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2012.677025. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22494466 Review.
-
Development of Prodrugs for Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: New Inorganic Scaffolds for Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation.J Pharm Sci. 2022 May;111(5):1262-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2022.02.005. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35182542 Review.
-
Advances in prodrug design for Parkinson's disease.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018 Apr;13(4):295-305. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1429400. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29361853 Review.
-
Evaluation of rat striatal L-dopa and DA concentration after intraperitoneal administration of L-dopa prodrugs in liposomal formulations.J Control Release. 2004 Sep 30;99(2):293-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.07.010. J Control Release. 2004. PMID: 15380638
-
The Design and Evaluation of an l-Dopa-Lazabemide Prodrug for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2017 Nov 27;22(12):2076. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122076. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29186917 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Potential of Genome Editing in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 26;22(17):9241. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179241. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Management of Parkinson's Disease: An Overview of the Current Advancements in Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 15;15(5):1503. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051503. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The knowledge driven DBTL cycle provides mechanistic insights while optimising dopamine production in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 May 16;24(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02729-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40380156 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Neuropathology Puzzle: A Systematic Review Uncovering the Pathological Culprits Behind the Neurological Disease.Cureus. 2023 Aug 29;15(8):e44353. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44353. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37664277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effect of levodopa on the basal ganglia-cerebellum connectivity in Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 May 6;11(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00954-9. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40328766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iversen L.L. Dopamine Handbook. Oxford University Press; Cary, NC, USA: 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

