Staphylococcus aureus produces pain through pore-forming toxins and neuronal TRPV1 that is silenced by QX-314
- PMID: 29295977
- PMCID: PMC5750211
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02448-6
Staphylococcus aureus produces pain through pore-forming toxins and neuronal TRPV1 that is silenced by QX-314
Abstract
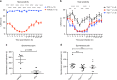
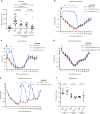
The hallmark of many bacterial infections is pain. The underlying mechanisms of pain during live pathogen invasion are not well understood. Here, we elucidate key molecular mechanisms of pain produced during live methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. We show that spontaneous pain is dependent on the virulence determinant agr and bacterial pore-forming toxins (PFTs). The cation channel, TRPV1, mediated heat hyperalgesia as a distinct pain modality. Three classes of PFTs-alpha-hemolysin (Hla), phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs), and the leukocidin HlgAB-directly induced neuronal firing and produced spontaneous pain. From these mechanisms, we hypothesized that pores formed in neurons would allow entry of the membrane-impermeable sodium channel blocker QX-314 into nociceptors to silence pain during infection. QX-314 induced immediate and long-lasting blockade of pain caused by MRSA infection, significantly more than lidocaine or ibuprofen, two widely used clinical analgesic treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
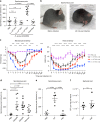
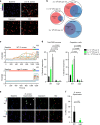
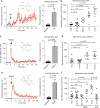
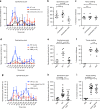


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI124606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI099394/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007308/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DP2 AT009499/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AI000904/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039518/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007180/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI121244/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K22 AI114810/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090255/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

