'Borono-lectin' based engineering as a versatile platform for biomedical applications
- PMID: 29296128
- PMCID: PMC5738650
- DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2017.1411143
'Borono-lectin' based engineering as a versatile platform for biomedical applications
Abstract
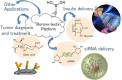
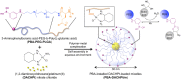
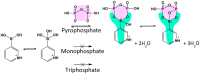
Boronic acids are well known for their ability to reversibly interact with the diol groups, a common motif of biomolecules including sugars and ribose. Due to their ability to interact with carbohydrates, they can be regarded as synthetic mimics of lectins, termed 'borono-lectins'. The borono-lectins can be tailored to elicit a broad profile of binding strength and specificity. This special property has been translated into many creative biomedical applications in a way interactive with biology. This review provides a brief overview of recent efforts of polymeric materials-based engineering taking advantage of such virtue of 'borono-lectins' chemistry, related to the field of biomaterials and drug delivery applications.
Keywords: 212 Surface and interfaces; 30 Bio-inspired and biomedical materials; Boronic acids; borono-lectins; diabetes; drug delivery systems; insulin; siRNA; sialic acids.
Figures






References
-
- Boeseken J. The use of boric acid for the determination of the configuration of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem 1949;4:189–210.
-
- Lorand JP, Edwards JO. Polyol complexes and structure of the benzeneboronate ion. J Org Chem. 1959;24(6):769–774.10.1021/jo01088a011 - DOI
-
- Foster AB. Zone electrophoresis of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1957;12:81–115. - PubMed
-
- Aronoff S, Chen TC, Cheveldayoff M. Complexation of D-glucose with borate. Carbohyd Res. 1975;40(2):299–309.10.1016/S0008-6215(00)82611-7 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
