Gamma knife radiosurgery for intralabyrinthine schwannomas
- PMID: 29296322
- PMCID: PMC5725321
Gamma knife radiosurgery for intralabyrinthine schwannomas
Abstract
Object: To analyze indications and technical specificities of treatment of intralabyrinthine schwannoma (ILS) by Gamma Knife radiosurgery.
Methods: Six patients were treated by Gamma Knife irradiation for a schwannoma arising from the cochleo-vestibular structures. Patients presented hearing worsening at different stages, tinnitus, imbalance and/or vertigo.
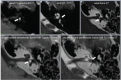
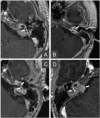
Results: ILS was intravestibular/intracochlear/intravestibulocochlear/ transmacular in respectively 2/1/2/1 patients. We cover the entire tumor volume with a margin prescription dose of 12-Gy. The tumor volume remained unchanged at last follow-up in all cases; for 4 patients with functional hearing still present before treatment, the audiological status remained stable in 2 patients, worsened moderately in 1 patientand worsened to cophosis in 1 patient. No patient experienced worsening of tinnitus, imbalance or vertigo after irradiation.
Conclusions: Gamma Knife treatment of ILS is technically feasible without risk thanks to the precision of current robotized Gamma Knife devices. Patients treated radiosurgically avoid some of the risks of microsurgery, could in some cases maintain useful hearing and prevent further symptoms worsening.
Keywords: Gamma Knife; Intralabyrinthine schwannomas; classification; cochlea; irradiation; outcome; radiosurgery; treatment; vestibule.
Figures

References
-
- Hamed A., Linthicum FH. Intralabyrinthine schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 2005; 26, 1085–1086. - PubMed
-
- Shin YR., Choi SJ., Park K., Choung YH. Intralabyrinthine schwannoma involving the cochlea, vestibule, and internal auditory canal: ‘canalolabyrinthine schwannoma’. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 266, 143–145. - PubMed
-
- Mayer O. Ein Fall von multiplen Tumoren in den Endausbreitungen des Akustikas. Z Ohrenheilkd. 1917; 5, 95–113.
-
- Di Lella F., Dispenza F., De Stefano A., Falcioni M., Sanna M. Management of intralabyrinthine schwannomas. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2007; 34, 459–463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
