Multisession stereotactic radiosurgery for large benign brain tumors of >3cm- early clinical outcomes
- PMID: 29296340
- PMCID: PMC5658851
Multisession stereotactic radiosurgery for large benign brain tumors of >3cm- early clinical outcomes
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical outcome of linear accelerator based multisession stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for large benign brain tumors of >3cm.
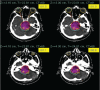
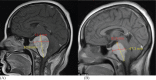
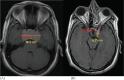
Methods: Between June 2009 and May 2011, 35 patients having large benign brain tumors of >3cm (≥15 cm3) were treated by multisession stereotactic radiosurgery. This retrospective study was carried out at Neurospinal & Medical Institute Karachi. There were 17 (48.6 %) males and 18(51.4 %) females. Median age was 36 years (range: 13-65 years). Median target volume was 49.4 cm3 (range: 15-184 cm3). The median marginal dose was 25 Gy (range: 20-27.5Gy) prescribed to a median 75% isodose line (range: 65-100 %). Median number of 5 fractions were used ranging 3-5 fractions.
Results: All the patients tolerated treatment very well. 21 (58.3%) patients had remarkable clinical improvement of neurological symptoms, 14 (38.9%) patients had stable symptoms, and only one patient had transient worsening of symptoms. No permanent neurological damage or radiation injury was seen. Radiologically, 9 (25.7%) patients achieved reduction in size of the tumor, 26(74.3 %) patients were having stable disease, and overall control rate was found to be 100 %. Median follow-up time from the end of SRS was 6.4 months (range: 1-22.5months).
Conclusion: Linear accelerator based multisession stereotactic radiosurgery for large benign brain tumors of >3cm is effective and well tolerated.
Keywords: Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS); benign brain tumors; brain tumors; linear accelerator; multi session SRS; radiation injury.
Figures




References
-
- Rahman M, Murad GJ, Mocco J. Early history of the sterotactic apparatus in neurosurgery. Neurosurg Focus 2009; 27(3):E12. - PubMed
-
- Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Chirug Scand. 1951; 102: 316-319. - PubMed
-
- Lozano AM, Gildenberg PL, Tasker RR, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Novotny J, Bhatanagar J, Lunsford LD. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: Technical Issues. Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2009. p. 1225-1235.
-
- Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Witt TC, Flickinger JC. The future of radiosurgery: radiobiology, technology, and applications. Surg Neurol. 2000; 54: 406-414. - PubMed
-
- Pollock BE, Lunsford LD. A call to define stereotacticradiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2004; 55:1371-1373. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
