Validity of the use of nose tip motion as a surrogate for intracranial motion in mask-fixated frameless Gamma Knife® Icon™ therapy
- PMID: 29296453
- PMCID: PMC5658824
Validity of the use of nose tip motion as a surrogate for intracranial motion in mask-fixated frameless Gamma Knife® Icon™ therapy
Abstract
This study investigates the validity of monitoring nose movement, using an infrared stereoscopic camera system (HDMM), to evaluate intracranial movement during treatment with the Icon™-model Gamma Knife®.
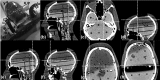
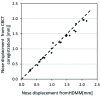
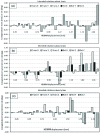
Methods: The HDMM was validated by comparison against known displacements. Next, an anthropomorphic phantom was rotated to register nose displacements on the HDMM, which were compared to the displacements of seven intracranial locations determined by cone-beam CT (CBCT). Similarly, CBCT-calculated intracranial displacements were compared against HDMM-reported nose displacements for patients.
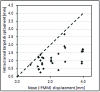
Results: HDMM-indicated displacements were accurate within 0.06mm mean. In the phantom, CBCT-calculated nose displacements agreed within 0.05mm (mean) of HDMM-reported nose displacements. In 16 instances intracranial displacements exceeded nose displacements; at the most extreme by 73% (2.76mm versus 1.59mm). Overall, intracranial anatomy displaced by 43% (mean) less than the nose. Patient data included no intracranial target displacements exceeding nose displacements.
Conclusions: Intracranial phantom and patient anatomy displaced by approximately half that of the nose, suggesting nose movement is generally a suitable surrogate for intracranial movement. The study constitutes the presentation of a simple, robust method that can be applied to determine the relationship between nose tip and intracranial motion in real patients undergoing frameless treatments on Icon™.
Keywords: Gamma Knife; Icon; cone beam CT; frameless stereotactic radiosurgery; intrafraction motion; mask; stereoscopic nose tracking.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosure of potential conflicts of interest Dr. Wright reports attendance at user group meetings of early Icon adopters and meetings organized and hosted by Elekta. All other authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures



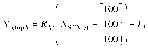
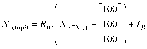

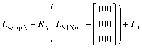
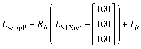
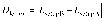


References
-
- Studholme C., Hill D., Hawkes D.: An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3D medical image alignment. Pattern Recognit. 1999;32(1),71–86
-
- Minniti G., D’Angelillo R., Scaringi C., et al. : Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2014;117,295–301 - PubMed
-
- Ruschin M, Nayebi N, Carlsson P., et al. : Performance of a novel repositioning head frame for Gamma Knife Perfexion and image-guided linac-based intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys. 2010;78(1),306–13 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
