Inotuzumab ozogamicin in adults with relapsed or refractory CD22-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a phase 1/2 study
- PMID: 29296758
- PMCID: PMC5728308
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016001925
Inotuzumab ozogamicin in adults with relapsed or refractory CD22-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a phase 1/2 study
Abstract
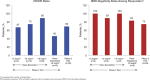
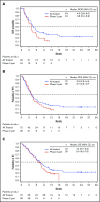
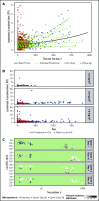
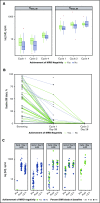
This study evaluated the safety, antitumor activity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of inotuzumab ozogamicin (InO) for CD22-positive relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In phase 1, patients received InO 1.2 (n = 3), 1.6 (n = 12), or 1.8 (n = 9) mg/m2 per cycle on days 1, 8, and 15 over a 28-day cycle (≤6 cycles). The recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) was confirmed (expansion cohort; n = 13); safety and activity of InO were assessed in patients receiving the RP2D in phase 2 (n = 35) and in all treated patients (n = 72). The RP2D was 1.8 mg/m2 per cycle (0.8 mg/m2 on day 1; 0.5 mg/m2 on days 8 and 15), with reduction to 1.6 mg/m2 per cycle after complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete marrow recovery (CRi). Treatment-related toxicities were primarily cytopenias. Four patients experienced treatment-related venoocclusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (VOD/SOS; 1 fatal). Two VOD/SOS events occurred during treatment without intervening transplant; of 24 patients proceeding to poststudy transplant, 2 experienced VOD/SOS after transplant. Forty-nine (68%) patients had CR/CRi, with 41 (84%) achieving minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity. Median progression-free survival was 3.9 (95% confidence interval, 2.9-5.4) months; median overall survival was 7.4 (5.7-9.2) months for all treated patients, with median 23.7 (range, 6.8-29.8) months of follow-up for all treated patients alive at data cutoff. Achievement of MRD negativity was associated with higher InO exposure. InO was well tolerated and demonstrated high single-agent activity and MRD-negativity rates. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01363297.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.J.D. served as a consultant for Pfizer, Novartis, Baxalta, BMS, and Amgen. W.S. received honoraria from ADC Therapeutics, Amgen, Gilead Sciences, Sigma-Tau and received royalties for a chapter in Up to Date; A.S.S. received honoraria, research funding, travel, accommodations, and expenses, served as a consultant for Amgen and Stemline Therapeutics, and received research funding, travel, accommodations, expenses, and served as a consultant for Amgen, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Stemline Therapeutics. M.L. has received research funding and served as a consultant for Pfizer. C.A.S. has received research funding from Pfizer and Amgen and served as a consultant for Pfizer. E.V., K.L., R.A., J.B., A.D.L., and L.F. are employees and stockholders of Pfizer. H.M.K. has received research funding from Pfizer, Amgen, Astex, Novartis, and BMS. A.S.A. has received research funding and served as a consultant for Pfizer. A.S. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program: Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/alyl.html. Accessed March 7, 2016.
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5-29. - PubMed
-
- Gökbuget N, Stanze D, Beck J, et al. ; German Multicenter Study Group for Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Outcome of relapsed adult lymphoblastic leukemia depends on response to salvage chemotherapy, prognostic factors, and performance of stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(10):2032-2041. - PubMed
-
- Bassan R, Hoelzer D. Modern therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(5):532-543. - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, et al. ; ECOG; MRC/NCRI Adult Leukemia Working Party. Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993. Blood. 2005;106(12):3760-3767. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

