Data-driven quality improvement in low-and middle-income country health systems: lessons from seven years of implementation experience across Mozambique, Rwanda, and Zambia
- PMID: 29297319
- PMCID: PMC5763308
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-017-2661-x
Data-driven quality improvement in low-and middle-income country health systems: lessons from seven years of implementation experience across Mozambique, Rwanda, and Zambia
Abstract
Background: Well-functioning health systems need to utilize data at all levels, from the provider, to local and national-level decision makers, in order to make evidence-based and needed adjustments to improve the quality of care provided. Over the last 7 years, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation's African Health Initiative funded health systems strengthening projects at the facility, district, and/or provincial level to improve population health. Increasing data-driven decision making was a common strategy in Mozambique, Rwanda and Zambia. This paper describes the similar and divergent approaches to increase data-driven quality of care improvements (QI) and implementation challenge and opportunities encountered in these three countries.
Methods: Eight semi-structured in-depth interviews (IDIs) were administered to program staff working in each country. IDIs for this paper included principal investigators of each project, key program implementers (medically-trained support staff, data managers and statisticians, and country directors), as well as Ministry of Health counterparts. IDI data were collected through field notes; interviews were not audio recorded. Data were analyzed using thematic analysis but no systematic coding was conducted. IDIs were supplemented through donor report abstractions, a structured questionnaire, one-on-one phone calls, and email exchanges with country program leaders to clarify and expand on key themes emerging from IDIs.
Results: Project successes ranged from over 450 collaborative action-plans developed, implemented, and evaluated in Mozambique, to an increase from <10% to >80% of basic clinical protocols followed in intervention facilities in rural Zambia, and a shift from a lack of awareness of health data among health system staff to collaborative ownership of data and using data to drive change in Rwanda.
Conclusion: Based on common successes across the country experiences, we recommend future data-driven QI interventions begin with data quality assessments to promote that rapid health system improvement is possible, ensure confidence in available data, serve as the first step in data-driven targeted improvements, and improve staff data analysis and visualization skills. Explicit Ministry of Health collaborative engagement can ensure performance review is collaborative and internally-driven rather than viewed as an external "audit."
Keywords: Data assessment; Decision making; Health systems research; Health systems strengthening; Low income; Maternal and child health; Mozambique; Quality improvement; Rwanda; Zambia.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Bradley H. Wagenaar, MPH, PhD; Lisa R. Hirschhorn, MD, MPH; Catherine Henley, MPH; Artur Gremu; Ntazana Sindano; Roma Chilengi, MBChB, MS.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
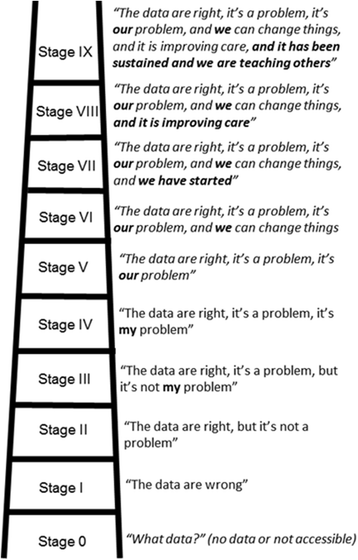
Figures

References
-
- Wagenaar BH, Sherr K, Fernandes Q, et al. Using routine health information systems for well-designed health evaluations in low- and middle-income countries. Health Policy Plan. 2015. pp. 1–7. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25887561. Accessed 24 Apr 2015. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shojania KG, Grimshaw JM. Evidence-based quality improvement: the state of the science. Health Affairs (Project Hope). 2005;24(1):138–50. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15647225. Accessed 1 July 2015. - PubMed
-
- Mutemwa RI. HMIS and decision-making in Zambia: re-thinking information solutions for district health management in decentralized health systems. Health Policy Plan. 2006;21(1):40–52. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16319088. Accessed 18 Nov 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

