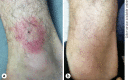
Tache Noire in a Patient with Acute Q Fever
- PMID: 29298443
- PMCID: PMC5968302
- DOI: 10.1159/000486573
Tache Noire in a Patient with Acute Q Fever
Abstract
Objective: To describe a rare case of acute Q fever with tache noire.
Clinical presentation and intervention: A 51-year-old man experienced acute Q fever showing tache noire, generally considered a pathognomonic sign of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF) and MSF-like illness, but not a clinical feature of Q fever. The patient was treated with doxycycline 100 mg every 12 h.
Conclusion: In the Mediterranean area, tache noire should be considered pathognomonic of MSF but it should not rule out Q fever. Clinical diagnosis should be supported by accurate laboratory diagnostic tests to guide proper management.
Keywords: Mediterranean spotted fever; Q fever; Tache noire.
© 2018 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Eklund CM, Parker RR, Lackman DB. A case of Q fever probably contracted by exposure to ticks in nature. Public Health Rep. 1947;62:1413–1416. - PubMed
-
- Technical Report. Risk Assessment on Q Fever. Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; 2010.
-
- Madeddu G, Fiore V, Mancini F, et al. Mediterranean spotted fever-like illness in Sardinia, Italy: a clinical and microbiological study. Infection. 2016;44:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Paris DH, Blacksell SD, Stenos J, et al. Real-time multiplex PCR assay for detection and differentiation of rickettsiae and orientiae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2008;102:186–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous