Phase I Trial of M7824 (MSB0011359C), a Bifunctional Fusion Protein Targeting PD-L1 and TGFβ, in Advanced Solid Tumors
- PMID: 29298798
- PMCID: PMC7985967
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2653
Phase I Trial of M7824 (MSB0011359C), a Bifunctional Fusion Protein Targeting PD-L1 and TGFβ, in Advanced Solid Tumors
Abstract
Purpose: M7824 (MSB0011359C) is an innovative first-in-class bifunctional fusion protein composed of a mAb against programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) fused to a TGFβ "trap."Experimental Design: In the 3+3 dose-escalation component of this phase I study (NCT02517398), eligible patients with advanced solid tumors received M7824 at 1, 3, 10, or 20 mg/kg once every 2 weeks until confirmed progression, unacceptable toxicity, or trial withdrawal; in addition, a cohort received an initial 0.3 mg/kg dose to evaluate pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics, followed by 10 mg/kg dosing. The primary objective is to determine the safety and maximum tolerated dose (MTD); secondary objectives include pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity, and best overall response.Results: Nineteen heavily pretreated patients with ECOG 0-1 have received M7824. Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in four patients (skin infection secondary to localized bullous pemphigoid, asymptomatic lipase increase, colitis with associated anemia, and gastroparesis with hypokalemia). The MTD was not reached. M7824 saturated peripheral PD-L1 and sequestered any released plasma TGFβ1, -β2, and -β3 throughout the dosing period at >1 mg/kg. There were signs of efficacy across all dose levels, including one ongoing confirmed complete response (cervical cancer), two durable confirmed partial responses (PR; pancreatic cancer; anal cancer), one near-PR (cervical cancer), and two cases of prolonged stable disease in patients with growing disease at study entry (pancreatic cancer; carcinoid).Conclusions: M7824 has a manageable safety profile in patients with heavily pretreated advanced solid tumors. Early signs of efficacy are encouraging, and multiple expansion cohorts are ongoing in a range of tumors. Clin Cancer Res; 24(6); 1287-95. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
I. Grenga is currently an employee of EMD Serono. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
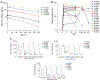
Figures


References
-
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, Hodi FS, Gutzmer R, Neyns B, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:375–84. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A, Grob JJ, Mortier L, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2521–32. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;387:1540–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

