Pretreatment albumin may aid in patient selection for intrahepatic Y-90 microsphere transarterial radioembolization (TARE) for malignancies of the liver
- PMID: 29299369
- PMCID: PMC5750191
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo.2017.06.18
Pretreatment albumin may aid in patient selection for intrahepatic Y-90 microsphere transarterial radioembolization (TARE) for malignancies of the liver
Abstract
Background: Hepatic malignancies are common including primary malignancies and metastases. Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) is an important treatment option. We reviewed safety and efficacy of (TARE) in our patients to identify factors that may impact treatment outcomes in a heterogeneous population.
Methods: All patients that received TARE at the Medical University of South Carolina from March 2006 through May of 2014 were included. Kaplan-Meier estimates on overall survival (OS) from date of first procedure are reported. Potential prognostic factors for OS were evaluated using log rank tests and Cox proportional hazards models.
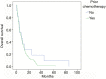
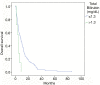
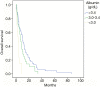
Results: In the 114 patients that received TARE at our institution, median follow-up was 6.4 months (range, 0-86 months) with the following histologies: colorectal (CR) n=55, hepatocellular (HC) n=20, cholangiocarcinoma (CC) n=16, neuroendocrine (NE) n=12, breast (BR) n=6, other n=5. At least 1 line of prior systemic therapy was noted in 79% of patients. Median OS was significantly better with NE and BR histology, and in those with normal albumin levels. With an albumin >3.4 median OS was 10.3 months, but was only 3.1 months with an albumin <3 g/dL. Grade ≥2 toxicity was observed in 22 patients (19.3%) including 9 (7.9%) with Grade 3 and 1 (0.9%) with Grade 4 toxicity.
Conclusions: TARE is a relatively safe and effective treatment for intrahepatic malignancies. Patients with NE and BR histology as well as those with better hepatic synthetic function were associated with significantly better survival. Our data suggest that patients with albumin below 3 g/dL may not derive significant benefit from TARE.
Keywords: Transarterial radioembolization; albumin; hepatic; malignancies; yttrium-90 (Y-90).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Data presented at ASCO GI Symposium 2015.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors impacting survival after transarterial radioembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from the prospective CIRT study.JHEP Rep. 2022 Nov 25;5(2):100633. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100633. eCollection 2023 Feb. JHEP Rep. 2022. PMID: 36593888 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Toxicities after 90Y Transarterial Radioembolization of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in the RESIN Registry.Radiology. 2022 Oct;305(1):228-236. doi: 10.1148/radiol.220387. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35762890
-
Factors Impacting Survival After Transarterial Radioembolization in Patients with Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Combined Analysis of the Prospective CIRT Studies.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Mar;47(3):310-324. doi: 10.1007/s00270-023-03657-x. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38321223 Free PMC article.
-
Any role for transarterial radioembolization in unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the era of advanced systemic therapies?World J Hepatol. 2023 Dec 27;15(12):1284-1293. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1284. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 38223418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Adv Ther. 2016 May;33(5):699-714. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0324-7. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Adv Ther. 2016. PMID: 27039186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AAPM Medical Physics Practice Guideline 14.a: Yttrium-90 microsphere radioembolization.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Feb;25(2):e14157. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14157. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 37820316 Free PMC article.
-
A pooled analysis of transarterial radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres for the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jun 7;12:4489-4498. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S202875. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31239717 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with yttrium-90 radioembolization: results from a large cohort over 13 years at a single center.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021 Aug;12(4):1718-1731. doi: 10.21037/jgo-20-435. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34532122 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources