Effect of Apium graveolens and Trachyspermum copticom on clinical symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia
- PMID: 29299438
- PMCID: PMC5745539
Effect of Apium graveolens and Trachyspermum copticom on clinical symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed at investigating the effect of Iranian traditional remedy prepared from Apium graveolens and Trachyspermum copticom (AT) on the severity and frequency of symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia (FD).
Material and methods: In total, 150 FD patients were included in this randomized double-blind trial, based on the ROME III diagnostic criteria, and they were divided into three intervention groups namely, AT, Placebo and omeprazole. Then, severity and frequency of symptoms during this eight-week trial were measured. Obtained information was analyzed using Chi-square test and repeated measures test.
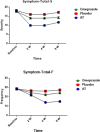
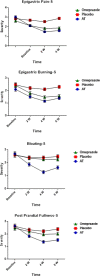
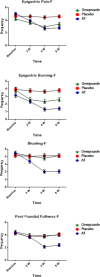
Result: In general, the severity and frequency of symptoms after the 4th week significantly decreased in the AT group as compared to the omeprazole and placebo groups, and continued to reduce by the end of the eighth week. General reduction of symptom severity and frequency in the omeprazole group was significantly different from the placebo group by the end of the 4th and 8th weeks. With respect to each individual symptom, AT markedly improved symptoms, such as burning, pain, early satiation, fullness, bloating, belching and nausea, as compared to placebo-treated group. Moreover, AT significantly improved symptoms, like vomiting, and nausea, except for pain, as compared to omeprazole-treated subjects.
Conclusion: According to the results, AT, as Iranian traditional remedy, was more effective than omeprazole and placebo in reducing the symptoms in FD patients.
Keywords: Apium graveolens; Carum copticom; Functional Dyspepsia; Iranian Traditional medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Alavinezhad A, Boskabadi MH. Ant-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Immunological Effects of Carum copticum L and Some of Its Constituents. Phytother Res. 2014;28:1739–1748. - PubMed
-
- Balaji G, Chalamaian M, Ramesh B. Antidiarrheal activity of ethanol and aqueous extracts of Carum copticum seeds in experimental rats. APJTB. 2012;2:1151–1155.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources