Association of loneliness with all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29300743
- PMCID: PMC5754055
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190033
Association of loneliness with all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Loneliness has social and health implications. The aim of this article is to evaluate the association of loneliness with all-cause mortality.
Methods: Pubmed, PsycINFO, CINAHL and Scopus databases were searched through June 2016 for published articles that measured loneliness and mortality. The main characteristics and the effect size values of each article were extracted. Moreover, an evaluation of the quality of the articles included was also carried out. A meta-analysis was performed firstly with all the included articles and secondly separating by gender, using a random effects model.
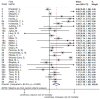
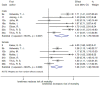
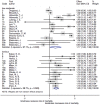
Results: A total of 35 articles involving 77220 participants were included in the systematic review. Loneliness is a risk factor for all-cause mortality [pooled HR = 1.22, 95% CI = (1.10, 1.35), p < 0.001] for both genders together, and for women [pooled HR = 1.26, 95% CI = (1.07, 1.48); p = 0.005] and men [pooled HR = 1.44; 95% CI = (1.19, 1.76); p < 0.001] separately.
Conclusions: Loneliness shows a harmful effect for all-cause mortality and this effect is slightly stronger in men than in women. Moreover, the impact of loneliness was independent from the quality evaluation of each article and the effect of depression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Andersson L. Loneliness research and interventions: a review of the literature. Aging & Mental Health. 1998;2(4):264–74.
-
- Hansen T, Slagsvold B. Late-Life Loneliness in 11 European Countries: Results from the Generations and Gender Survey. Social Indicators Research. 2016:445–64. doi: 10.1007/s11205-015-1111-6 - DOI
-
- Linehan T, Bottery S, Kaye A, Millar L, Sinclair D, Watson J. 2030 vision: The best and worst futures for older people in the UK 2014. http://www.ilcuk.org.uk/index.php/publications/publication_details/2030_....
-
- Cacioppo JT, Hughes ME, Waite LJ, Hawkley LC, Thisted RA. Loneliness as a specific risk factor for depressive symptoms: cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Psychology and aging. 2006;21(1):140–51. . - PubMed
-
- Cacioppo JT, Hawkley LC, Thisted RA. Perceived social isolation makes me sad: 5-year cross-lagged analyses of loneliness and depressive symptomatology in the Chicago Health, Aging, and Social Relations Study. Psychology and aging. 2010;25(2):453–63. doi: 10.1037/a0017216 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

