Aberrant Epigenetic Gene Regulation in GABAergic Interneuron Subpopulations in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Mouse Offspring Following Developmental Exposure to Hexachlorophene
- PMID: 29301063
- PMCID: PMC5917777
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx291
Aberrant Epigenetic Gene Regulation in GABAergic Interneuron Subpopulations in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Mouse Offspring Following Developmental Exposure to Hexachlorophene
Abstract
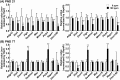
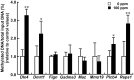
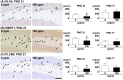
Maternal hexachlorophene (HCP) exposure causes transient disruption of hippocampal neurogenesis in mouse offspring. We examined epigenetically hypermethylated and downregulated genes related to this HCP-induced disrupted neurogenesis. Mated female mice were dietary exposed to 0 or 100 ppm HCP from gestational day 6 to postnatal day (PND) 21 on weaning. The hippocampal dentate gyrus of male offspring was subjected to methyl-capture sequencing and real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analyses on PND 21. Validation analyses on methylation identified three genes, Dlx4, Dmrt1, and Plcb4, showing promoter-region hypermethylation. Immunohistochemically, DLX4+, DMRT1+, and PLCB4+ cells in the dentate hilus co-expressed GAD67, a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic neuron marker. HCP decreased all of three subpopulations as well as GAD67+ cells on PND 21. PLCB4+ cells also co-expressed the metabotropic glutamate receptor, GRM1. HCP also decreased transcript level of synaptic plasticity-related genes in the dentate gyrus and immunoreactive granule cells for synaptic plasticity-related ARC. On PND 77, all immunohistochemical cellular density changes were reversed, whereas the transcript expression of the synaptic plasticity-related genes fluctuated. Thus, HCP-exposed offspring transiently reduced the number of GABAergic interneurons. Among them, subpopulations expressing DLX4, DMRT1, or PLCB4 were transiently reduced in number through an epigenetic mechanism. Considering the role of the Dlx gene family in GABAergic interneuron migration and differentiation, the decreased number of DLX4+ cells may be responsible for reducing those GABAergic interneurons regulating neurogenesis. The effect on granule cell synaptic plasticity was sustained until the adult stage, and reduced GABAergic interneurons active in GRM1-PLCB4 signaling may be responsible for the suppression on weaning.
Figures




References
-
- Akane H., Shiraki A., Imatanaka N., Akahori Y., Itahashi M., Ohishi T., Mitsumori K., Shibutani M. (2013a). Glycidol induces axonopathy by adult-stage exposure and aberration of hippocampal neurogenesis affecting late-stage differentiation by developmental exposure in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 134, 140–154. - PubMed
-
- Akane H., Saito F., Yamanaka H., Shiraki A., Imatanaka N., Akahori Y., Morita R., Mitsumori K., Shibutani M. (2013b). Methacarn as a whole brain fixative for gene and protein expression analyses of specific brain regions in rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 38, 431–443. - PubMed
-
- Anderson S., Eisenstat D., Shi L., Rubenstein J. (1997). Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: Dependence on Dlx genes. Science 278, 474–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

