An Antimicrobial Peptide and Its Neuronal Receptor Regulate Dendrite Degeneration in Aging and Infection
- PMID: 29301098
- PMCID: PMC5757245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.12.001
An Antimicrobial Peptide and Its Neuronal Receptor Regulate Dendrite Degeneration in Aging and Infection
Abstract
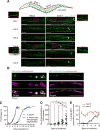
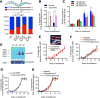
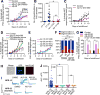
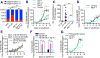
Infections have been identified as possible risk factors for aging-related neurodegenerative diseases, but it remains unclear whether infection-related immune molecules have a causative role in neurodegeneration during aging. Here, we reveal an unexpected role of an epidermally expressed antimicrobial peptide, NLP-29 (neuropeptide-like protein 29), in triggering aging-associated dendrite degeneration in C. elegans. The age-dependent increase of nlp-29 expression is regulated by the epidermal tir-1/SARM-pmk-1/p38 MAPK innate immunity pathway. We further identify an orphan G protein-coupled receptor NPR-12 (neuropeptide receptor 12) acting in neurons as a receptor for NLP-29 and demonstrate that the autophagic machinery is involved cell autonomously downstream of NPR-12 to transduce degeneration signals. Finally, we show that fungal infections cause dendrite degeneration using a similar mechanism as in aging, through NLP-29, NPR-12, and autophagy. Our findings reveal an important causative role of antimicrobial peptides, their neuronal receptors, and the autophagy pathway in aging- and infection-associated dendrite degeneration.
Keywords: AMP; G protein-coupled receptor; GPCR; aging; antimicrobial peptide; autophagy; dendrite degeneration; infection.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
G-Protein-Coupled Receptor SRBC-48 Protects against Dendrite Degeneration and Reduced Longevity Due to Infection.Cell Rep. 2020 May 19;31(7):107662. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107662. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32433971 Free PMC article.
-
TLR-independent control of innate immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans by the TIR domain adaptor protein TIR-1, an ortholog of human SARM.Nat Immunol. 2004 May;5(5):488-94. doi: 10.1038/ni1060. Epub 2004 Mar 28. Nat Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15048112
-
Global analysis of neuropeptide receptor conservation across phylum Nematoda.BMC Biol. 2024 Oct 8;22(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02017-6. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39379997 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in axonal and dendritic degeneration.Trends Neurosci. 2013 Jul;36(7):418-28. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23639383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of aging and innate immunity in C. elegans.Aging Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):185-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00108.x. Aging Cell. 2004. PMID: 15268752 Review.
Cited by
-
Colonization of the Caenorhabditis elegans gut with human enteric bacterial pathogens leads to proteostasis disruption that is rescued by butyrate.PLoS Pathog. 2021 May 6;17(5):e1009510. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009510. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33956916 Free PMC article.
-
Valorization of Polysaccharides From Benincasa hispida: Physicochemical, Moisturizing, and Antioxidant Skincare Properties.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 17;13:912382. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.912382. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784722 Free PMC article.
-
A knock-in translational reporter for NLP-29 reveals AMP secretion to the apical extracellular matrices following epidermal damage in Caenorhabditis elegans.MicroPubl Biol. 2025 Mar 29;2025:10.17912/micropub.biology.001435. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001435. eCollection 2025. MicroPubl Biol. 2025. PMID: 40226512 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-1-dependent immune evasion induced by fungal infection leads to cell loss in the Drosophila brain.PLoS Biol. 2025 Feb 13;23(2):e3003020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003020. eCollection 2025 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 39946503 Free PMC article.
-
Insect Behavioral Change and the Potential Contributions of Neuroinflammation-A Call for Future Research.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;12(4):465. doi: 10.3390/genes12040465. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adalbert R, Coleman MP. Review: Axon pathology in age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2013;39:90–108. - PubMed
-
- Apfeld J, Kenyon C. Cell nonautonomy of C. elegans daf-2 function in the regulation of diapause and life span. Cell. 1998;95:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger LM. Immune proteins in brain development and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 2009;64:93–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

