Cytotoxic, Apoptotic and Genotoxic Effects of Lipid-Based and Polymeric Nano Micelles, an In Vitro Evaluation
- PMID: 29301191
- PMCID: PMC5874780
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics6010007
Cytotoxic, Apoptotic and Genotoxic Effects of Lipid-Based and Polymeric Nano Micelles, an In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
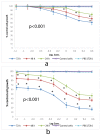
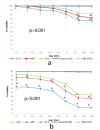
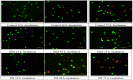
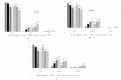
Self-assembly systems (SAS) mainly consist of micelles, and liposomes are the classes of Nano Drug Delivery Systems with superior properties compared to traditional therapeutics in targeting cancer tumors. All commercially available nano-formulations of chemotherapeutics currently consist of SAS. According to our knowledge, a specific toxicity comparison based on material differences has not yet been performed. The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the toxicity of two SAS consisting of Sterically Stabilized Micelles (SSM) made of a lipid-based amphiphilic distearoyl-sn-glycero-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol (PEG)-2000 and a polymeric micelle (PM) consisting of Y-shape amphiphilic block copolymer, synthesized using poly ε-caprolactone and PEG. The mechanism of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of micelles on L-929 healthy mouse fibroblast cells was assessed using Sulforhodamine-B, WST-1, Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide and alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis assays. Results showed that SSM in conc. of 40 mg/mL shows very low cytotoxicity at the end of 24, 48 and 72 h. The DNA damage caused by SSM was much lower than PM while the latter one showed significant toxicity by causing apoptosis with the ED50 value of 3 mg/mL. While the DNA damage caused by SSM was ignorable, some DNA chain breaks were detected on cells treated with PM.
Keywords: Nano Drug Delivery System; cytotoxicity; genotoxicity; lipid-based micelles; polymeric micelle; targeted cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
PEG-b-PCL polymeric nano-micelle inhibits vascular angiogenesis by activating p53-dependent apoptosis in zebrafish.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Dec 5;11:6517-6531. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S112658. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27980407 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and in vitro experiments of carcinoma vascular endothelial targeting polymeric nano-micelles combining small particle size and supermagnetic sensitivity.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Mar 8;15(5):498-506. doi: 10.7150/ijms.23146. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29559839 Free PMC article.
-
Sterically stabilized phospholipid mixed micelles: in vitro evaluation as a novel carrier for water-insoluble drugs.Pharm Res. 2003 Feb;20(2):297-302. doi: 10.1023/a:1022243709003. Pharm Res. 2003. PMID: 12636171
-
Progress of drug-loaded polymeric micelles into clinical studies.J Control Release. 2014 Sep 28;190:465-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.042. Epub 2014 Jun 30. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24993430 Review.
Cited by
-
Paeoniflorin Antagonizes TNF-α-Induced L929 Fibroblastoma Cells Apoptosis by Inhibiting NF-κBp65 Activation.Dose Response. 2018 Jun 4;16(2):1559325818774977. doi: 10.1177/1559325818774977. eCollection 2018 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2018. PMID: 29887769 Free PMC article.
-
Hemolytic Properties of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in In Vitro Systems.Toxics. 2024 Mar 27;12(4):246. doi: 10.3390/toxics12040246. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38668469 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles and Liposomes for Bone Diseases Treatment.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 7;10(12):3158. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123158. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Cancer Treatment with Nanotechnology: The Role of Berberine as a Star Natural Compound.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 22;19:8621-8640. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S469350. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39188860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Comoglu T., Bahadori F. NanoVectors for Neurotherapeutic Delivery, Part I: Liposomes and Micelles. OMICS International; Los Angeles, CA, USA: 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

