Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management
- PMID: 29301630
- PMCID: PMC7958889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.011
Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management
Abstract
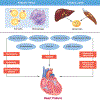
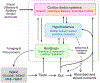
Obesity continues to be among the top health concerns across the globe. Despite our failure to contain the high prevalence of obesity, we now have a better understanding of its pathophysiology, and how excess adiposity leads to type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle modification is recommended as the cornerstone of obesity management, but many patients do not achieve long-lasting benefits due to difficulty with adherence as well as physiological and neurohormonal adaptation of the body in response to weight loss. Fortunately, 5 drug therapies-orlistat, lorcaserin, liraglutide, phentermine/topiramate, and naltrexone/bupropion-are available for long-term weight management. Additionally, several medical devices are available for short-term and long-term use. Bariatric surgery yields substantial and sustained weight loss with resolution of type 2 diabetes, although due to the high cost and a small risk of serious complications, it is generally recommended for patients with severe obesity. Benefit-to-risk balance should guide treatment decisions.
Keywords: adipose tissue; antiobesity drugs; bariatric surgery; obesity; overweight; weight loss.
Copyright © 2018 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Heymsfield SB, Wadden TA. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

