Thy1-Targeted Microbubbles for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 29301827
- PMCID: PMC5884723
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2057
Thy1-Targeted Microbubbles for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
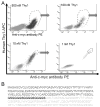
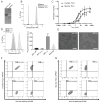
Purpose: To engineer a dual human and murine Thy1-binding single-chain-antibody ligand (Thy1-scFv) for contrast microbubble-enhanced ultrasound molecular imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).Experimental Design: Thy1-scFv were engineered using yeast-surface-display techniques. Binding to soluble human and murine Thy1 and to Thy1-expressing cells was assessed by flow cytometry. Thy1-scFv was then attached to gas-filled microbubbles to create MBThy1-scFv Thy1 binding of MBThy1-scFv to Thy1-expressing cells was evaluated under flow shear stress conditions in flow-chamber experiments. MBscFv-scrambled and MBNon-targeted were used as negative controls. All microbubble types were tested in both orthotopic human PDAC xenografts and transgenic PDAC mice in vivoResults: Thy1-scFv had a KD of 3.4 ± 0.36 nmol/L for human and 9.2 ± 1.7 nmol/L for murine Thy1 and showed binding to both soluble and cellularly expressed Thy1. MBThy1-scFv was attached to Thy1 with high affinity compared with negative control microbubbles (P < 0.01) as assessed by flow cytometry. Similarly, flow-chamber studies showed significantly (P < 0.01) higher binding of MBThy1-scFv (3.0 ± 0.81 MB/cell) to Thy1-expressing cells than MBscFv-scrambled (0.57 ± 0.53) and MBNon-targeted (0.43 ± 0.53). In vivo ultrasound molecular imaging using MBThy1-scFv demonstrated significantly higher signal (P < 0.01) in both orthotopic (5.32 ± 1.59 a.u.) and transgenic PDAC (5.68 ± 2.5 a.u.) mice compared with chronic pancreatitis (0.84 ± 0.6 a.u.) and normal pancreas (0.67 ± 0.71 a.u.). Ex vivo immunofluorescence confirmed significantly (P < 0.01) increased Thy1 expression in PDAC compared with chronic pancreatitis and normal pancreas tissue.Conclusions: A dual human and murine Thy1-binding scFv was designed to generate contrast microbubbles to allow PDAC detection with ultrasound. Clin Cancer Res; 24(7); 1574-85. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Toward the Clinical Development and Validation of a Thy1-Targeted Ultrasound Contrast Agent for the Early Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Invest Radiol. 2020 Nov;55(11):711-721. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000697. Invest Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32569010 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice by ultrasound imaging of thymocyte differentiation antigen 1.Gastroenterology. 2013 Oct;145(4):885-894.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23791701 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and purification of a native Thy1-single-chain variable fragment for use in molecular imaging.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 29;11(1):23026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02445-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34845270 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of targeted microbubbles in diagnostic molecular imaging of pancreatic cancer.Bioeng Transl Med. 2020 Sep 7;6(1):e10183. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10183. eCollection 2021 Jan. Bioeng Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33532585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in molecular imaging with ultrasound.Mol Imaging. 2010 Jun;9(3):117-27. Mol Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20487678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Ultrasound Imaging.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Sep 28;10(10):1935. doi: 10.3390/nano10101935. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32998422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gas-Stabilizing Sub-100 nm Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Ultrasound Theranostics.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 14;5(38):24762-24772. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03377. eCollection 2020 Sep 29. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33015494 Free PMC article.
-
X-aptamers targeting Thy-1 membrane glycoprotein in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Biochimie. 2021 Feb;181:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.11.018. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 33242496 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in early detection of pancreatic cancer: the role of artificial intelligence and novel imaging techniques.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Apr;50(4):1731-1743. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04644-7. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39467913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterial-assisted pancreatic cancer theranostics.Regen Biomater. 2025 Jun 11;12:rbaf054. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbaf054. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40585530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Shaib YH, Davila JA, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of pancreatic cancer in the United States: changes below the surface. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:87–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

