Engineering posttranslational proofreading to discriminate nonstandard amino acids
- PMID: 29301968
- PMCID: PMC5776986
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1715137115
Engineering posttranslational proofreading to discriminate nonstandard amino acids
Abstract
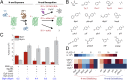
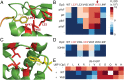
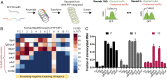
Incorporation of nonstandard amino acids (nsAAs) leads to chemical diversification of proteins, which is an important tool for the investigation and engineering of biological processes. However, the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases crucial for this process are polyspecific in regard to nsAAs and standard amino acids. Here, we develop a quality control system called "posttranslational proofreading" to more accurately and rapidly evaluate nsAA incorporation. We achieve this proofreading by hijacking a natural pathway of protein degradation known as the N-end rule, which regulates the lifespan of a protein based on its amino-terminal residue. We find that proteins containing certain desired N-terminal nsAAs have much longer half-lives compared with those proteins containing undesired amino acids. We use the posttranslational proofreading system to further evolve a Methanocaldococcus jannaschii tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (TyrRS) variant and a tRNATyr species for improved specificity of the nsAA biphenylalanine in vitro and in vivo. Our newly evolved biphenylalanine incorporation machinery enhances the biocontainment and growth of genetically engineered Escherichia coli strains that depend on biphenylalanine incorporation. Finally, we show that our posttranslational proofreading system can be designed for incorporation of other nsAAs by rational engineering of the ClpS protein, which mediates the N-end rule. Taken together, our posttranslational proofreading system for in vivo protein sequence verification presents an alternative paradigm for molecular recognition of amino acids and is a major advance in our ability to accurately expand the genetic code.
Keywords: N-end rule; genetic code expansion; nonstandard amino acids; protein degradation; synthetic biology.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: G.M.C. has related financial interests in ReadCoor, EnEvolv, and GRO Biosciences. A.M.K. and G.M.C. have filed a provisional patent on posttranslational proofreading, and A.M.K., D.S., E.K., and G.M.C. have filed a provisional patent on evolved BipA OTS variants. For a complete list of G.M.C.’s financial interests, please visit arep.med.harvard.edu/gmc/tech.html.
Figures
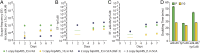
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

