Oncogene addiction and radiation oncology: effect of radiotherapy with photons and carbon ions in ALK-EML4 translocated NSCLC
- PMID: 29304828
- PMCID: PMC5756447
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-017-0947-0
Oncogene addiction and radiation oncology: effect of radiotherapy with photons and carbon ions in ALK-EML4 translocated NSCLC
Abstract
Background: Patients with Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4)-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) positive lung cancer are sensitive to ALK-kinase inhibitors. TAE684 is a potent second generation ALK inhibitor that overcomes Crizotinib resistance. Radiotherapy is an integral therapeutic component of locally advanced lung cancer. Therefore, we sought to investigate the effects of combined radiotherapy and ALK-inhibition via TAE684 in ALK-positive vs. wild type lung cancer cells.
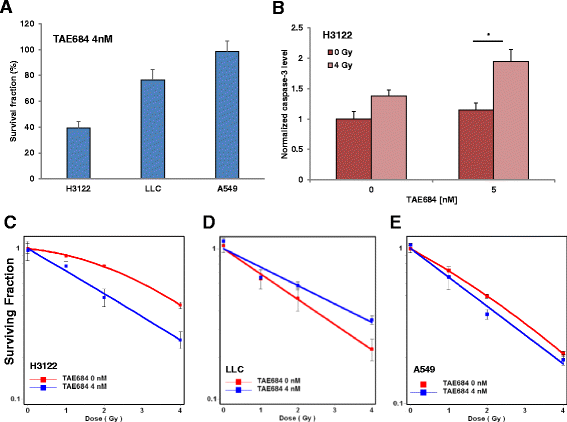
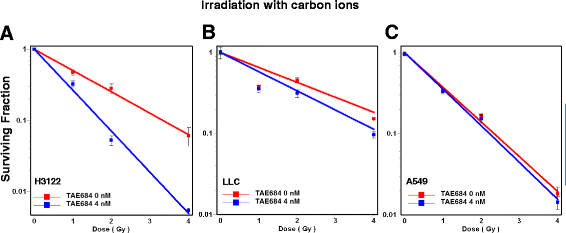
Methods: Human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines harboring wild-type ALK (A549), EML4-ALK translocation (H3122) and murine Lewis Lung Cancer (LLC) cells were investigated. Cells were irradiated with 1-4 Gy X-Rays (320 keV) and carbon ions (Spread-out Bragg Peak, SOBP (245.4-257.0 MeV/u)) at Heidelberg Ion Therapy center. TAE684 was administered at the dose range 0-100 nM. Clonogenic survival, proliferation and apoptosis via caspase 3/7 expression level were assessed in all three cell lines using time-lapse live microscopy.
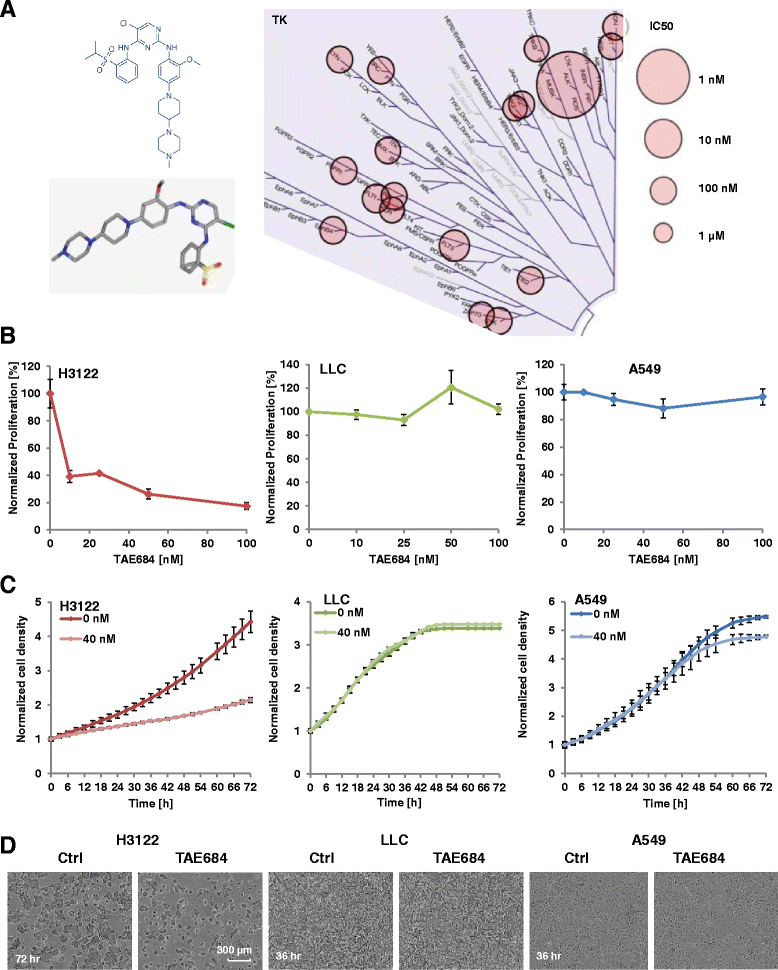
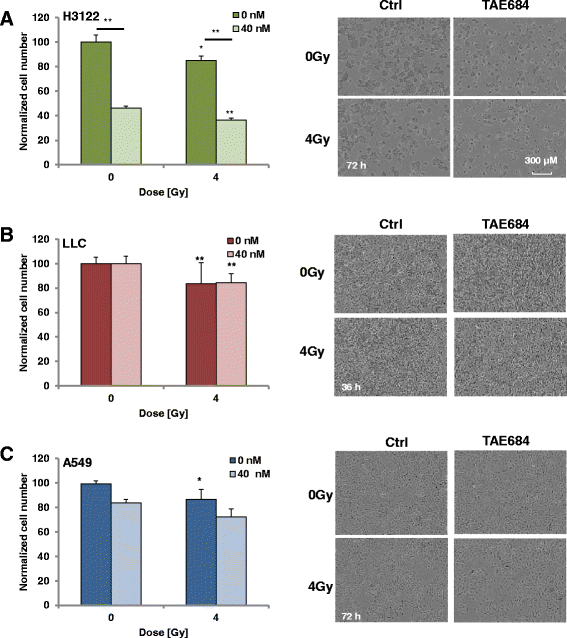
Results: TAE684 inhibited the proliferation of H3122 cells in a dose-dependent manner with a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ~ 8.2 nM. However, A549 and LLC cells were relatively resistant to TAE684 and IC50 was not reached at concentrations tested (up to 100 nM) in proliferation assay. The antiproliferative effect of TAE684 was augmented by radiotherapy in H3122 cells. TAE684 significantly sensitized H3122 cells to particle therapy with carbon ions (sensitizer enhancement ratio ~1.61, p < 0.05). Caspase 3/7 activity was evidently enhanced after combination therapy in H3122 cells.
Conclusions: This is the first report demonstrating synergistic effects of combined TAE684 and radiotherapy in EML4-ALK positive lung cancer cells. In addition to conventional photon radiotherapy, ALK-inhibition also enhanced the effects of particle irradiation using carbon ions. Our data indicate beneficial effects of combined ALK-inhibition and radiotherapy in treatment of this distinct subpopulation of NSCLC that warrant further evaluation.
Keywords: ALK inhibitors; Carbon ions; EML4-ALK-fusion; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of crizotinib and radiotherapy in experimental EML4-ALK fusion positive lung cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2015 Feb;114(2):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2014.12.009. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Radiother Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25592111
-
Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 15;18(22):6219-26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0392. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22843788
-
A new human lung adenocarcinoma cell line harboring the EML4-ALK fusion gene.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct;44(10):963-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyu110. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25170107
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement in lung cancer: its biological and clinical significance.Respir Investig. 2014 Nov;52(6):330-8. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Respir Investig. 2014. PMID: 25453376 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms that underpin EML4-ALK driven cancers and their response to targeted drugs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Mar;73(6):1209-24. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2117-6. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26755435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiosensitizing Effect of Gadolinium Oxide Nanocrystals in NSCLC Cells Under Carbon Ion Irradiation.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019 Oct 21;14(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-3152-2. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019. PMID: 31637533 Free PMC article.
-
CLPTM1L induces estrogen receptor β signaling-mediated radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Sep 17;18(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00571-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32943060 Free PMC article.
-
Charged Particle and Conventional Radiotherapy: Current Implications as Partner for Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 23;13(6):1468. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061468. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances progress of targeted drugs combined with radiotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a review.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 5;13:1285593. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1285593. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38115908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling of chemo-radiotherapy targeting growing vascular tumors: A continuum-level approach.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 15;20(1):e0301657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301657. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39813216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scorsetti M, Navarria P, Mancosu P, Alongi F, Castiglioni S, Cavina R, Cozzi L, Fogliata A, Pentimalli S, Tozzi A, Santoro A. Large volume unresectable locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: acute toxicity and initial outcome results with rapid arc. Radiat Oncol. 2010;5:94. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-94. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu YE, Lin Q, Meng FJ, Chen XJ, Ren XC, Cao B, Wang N, Zong J, Peng Y, Ku YJ, Chen Y. High-dose accelerated hypofractionated three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (at 3 Gy/fraction) with concurrent vinorelbine and carboplatin chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a feasibility study. Radiat Oncol. 2013;8:198. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-198. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Neubauer M, Yiannoutsos C, McGarry R, Arseneau J, Ansari R, Reynolds C, Govindan R, Melnyk A, Fisher W, et al. Phase III study of cisplatin, etoposide, and concurrent chest radiation with or without consolidation docetaxel in patients with inoperable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: the Hoosier Oncology Group and U.S. Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5755–5760. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7840. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

