Role and regulation of Abelson tyrosine kinase in Crk-associated substrate/profilin-1 interaction and airway smooth muscle contraction
- PMID: 29304860
- PMCID: PMC5756382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-017-0709-4
Role and regulation of Abelson tyrosine kinase in Crk-associated substrate/profilin-1 interaction and airway smooth muscle contraction
Abstract
Background: Airway smooth muscle contraction is critical for maintenance of appropriate airway tone, and has been implicated in asthma pathogenesis. Smooth muscle contraction requires an "engine" (myosin activation) and a "transmission system" (actin cytoskeletal remodeling). However, the mechanisms that control actin remodeling in smooth muscle are not fully elucidated. The adapter protein Crk-associated substrate (CAS) regulates actin dynamics and the contraction in smooth muscle. In addition, profilin-1 (Pfn-1) and Abelson tyrosine kinase (c-Abl) are also involved in smooth muscle contraction. The interplays among CAS, Pfn-1 and c-Abl in smooth muscle have not been previously investigated.
Methods: The association of CAS with Pfn-1 in mouse tracheal rings was evaluated by co-immunoprecipitation. Tracheal rings from c-Abl conditional knockout mice were used to assess the roles of c-Abl in the protein-protein interaction and smooth muscle contraction. Decoy peptides were utilized to evaluate the importance of CAS/Pfn-1 coupling in smooth muscle contraction.
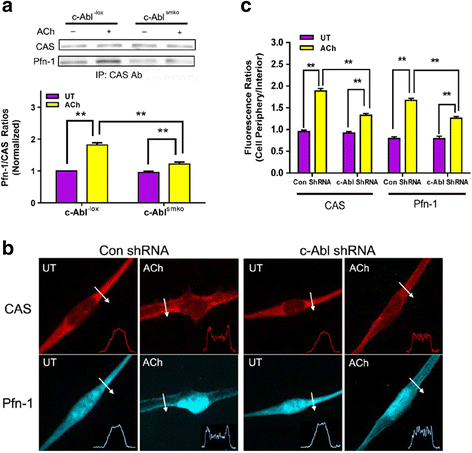
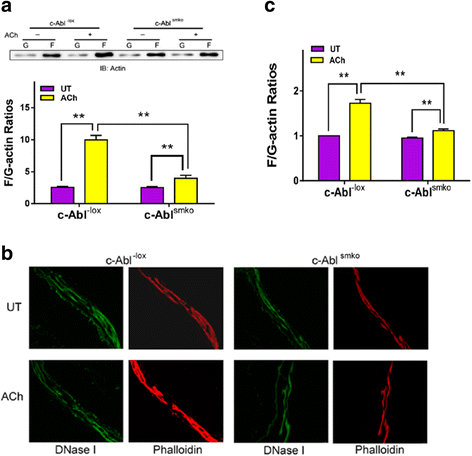
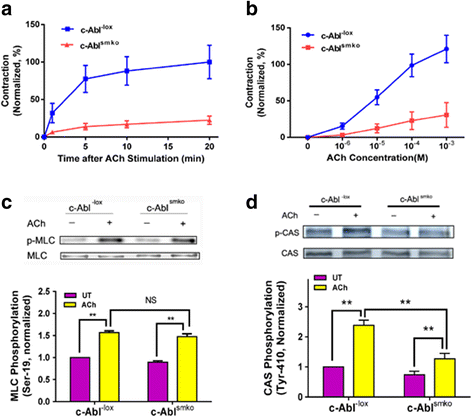
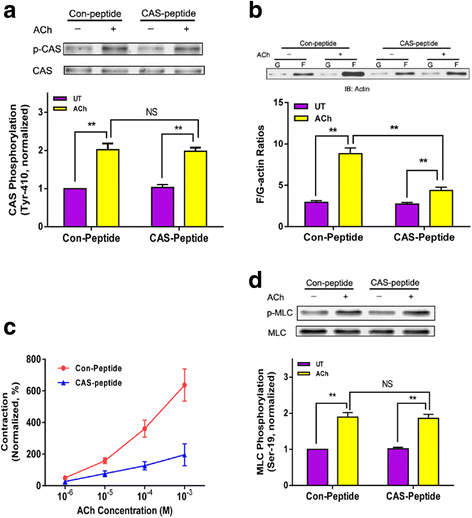
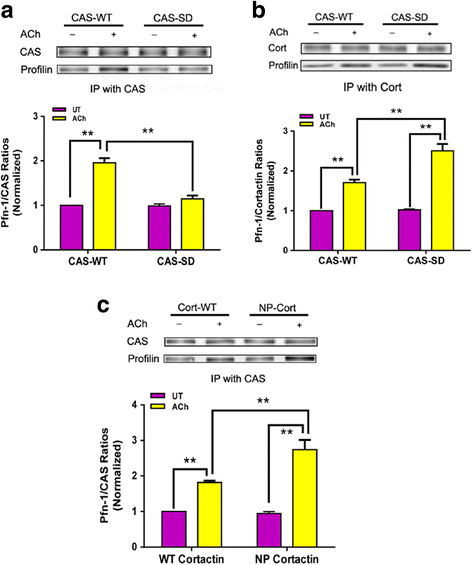
Results: Stimulation with acetylcholine (ACh) increased the interaction of CAS with Pfn-1 in smooth muscle, which was regulated by CAS tyrosine phosphorylation and c-Abl. The CAS/Pfn-1 coupling was also modified by the phosphorylation of cortactin (a protein implicated in Pfn-1 activation). In addition, ACh activation promoted the spatial redistribution of CAS and Pfn-1 in smooth muscle cells, which was reduced by c-Abl knockdown. Inhibition of CAS/Pfn-1 interaction by a decoy peptide attenuated the ACh-induced actin polymerization and contraction without affecting myosin light chain phosphorylation. Furthermore, treatment with the Src inhibitor PP2 and the actin polymerization inhibitor latrunculin A attenuated the ACh-induced c-Abl tyrosine phosphorylation (an indication of c-Abl activation).
Conclusions: Our results suggest a novel activation loop in airway smooth muscle: c-Abl promotes the CAS/Pfn-1 coupling and actin polymerization, which conversely facilitates c-Abl activation. The positive feedback may render c-Abl in active state after contractile stimulation.
Keywords: Actin cytoskeleton; Crk-associated substrate; Excitation-contraction coupling; Profilin-1; Smooth muscle; c-Abl kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The association of cortactin with profilin-1 is critical for smooth muscle contraction.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):14157-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548099. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24700464 Free PMC article.
-
Role of c-Abl tyrosine kinase in smooth muscle cell migration.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Apr 15;306(8):C753-61. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00327.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24477238 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the adapter protein Abi1 in actin-associated signaling and smooth muscle contraction.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20713-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439877. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23740246 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Actin Cytoskeleton in Smooth Muscle.Adv Pharmacol. 2018;81:1-38. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Adv Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29310796 Review.
-
Critical role of actin-associated proteins in smooth muscle contraction, cell proliferation, airway hyperresponsiveness and airway remodeling.Respir Res. 2015 Oct 30;16:134. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0296-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26517982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinctive roles of Abi1 in regulating actin-associated proteins during human smooth muscle cell migration.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 30;10(1):10667. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67781-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32606387 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane adhesion junctions regulate airway smooth muscle phenotype and function.Physiol Rev. 2023 Jul 1;103(3):2321-2347. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00020.2022. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36796098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperativity between β-agonists and c-Abl inhibitors in regulating airway smooth muscle relaxation.FASEB J. 2021 Jul;35(7):e21674. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100154R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34115899 Free PMC article.
-
Plk1 Mediates Paxillin Phosphorylation (Ser-272), Centrosome Maturation, and Airway Smooth Muscle Layer Thickening in Allergic Asthma.Sci Rep. 2019 May 17;9(1):7555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43927-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31101859 Free PMC article.
-
Plk1 Regulates Caspase-9 Phosphorylation at Ser-196 and Apoptosis of Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Feb;66(2):223-234. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0192OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34705620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang DC, Stull JT, Kubota Y, Kamm KE. Regulation of the Ca2+ dependence of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:11839–11845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

