Teaching the basics of reactive oxygen species and their relevance to cancer biology: Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species detection, redox signaling, and targeted therapies
- PMID: 29306792
- PMCID: PMC5756055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.012
Teaching the basics of reactive oxygen species and their relevance to cancer biology: Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species detection, redox signaling, and targeted therapies
Abstract
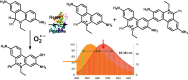
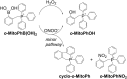
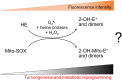
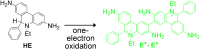
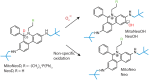
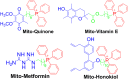
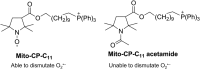
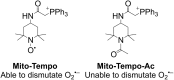
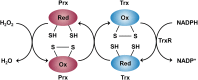
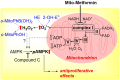
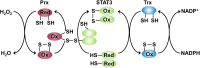
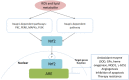
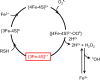
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been implicated in tumorigenesis (tumor initiation, tumor progression, and metastasis). Of the many cellular sources of ROS generation, the mitochondria and the NADPH oxidase family of enzymes are possibly the most prevalent intracellular sources. In this article, we discuss the methodologies to detect mitochondria-derived superoxide and hydrogen peroxide using conventional probes as well as newly developed assays and probes, and the necessity of characterizing the diagnostic marker products with HPLC and LC-MS in order to rigorously identify the oxidizing species. The redox signaling roles of mitochondrial ROS, mitochondrial thiol peroxidases, and transcription factors in response to mitochondria-targeted drugs are highlighted. ROS generation and ROS detoxification in drug-resistant cancer cells and the relationship to metabolic reprogramming are discussed. Understanding the subtle role of ROS in redox signaling and in tumor proliferation, progression, and metastasis as well as the molecular and cellular mechanisms (e.g., autophagy) could help in the development of combination therapies. The paradoxical aspects of antioxidants in cancer treatment are highlighted in relation to the ROS mechanisms in normal and cancer cells. Finally, the potential uses of newly synthesized exomarker probes for in vivo superoxide and hydrogen peroxide detection and the low-temperature electron paramagnetic resonance technique for monitoring oxidant production in tumor tissues are discussed.
Keywords: Mitochondrial inhibition; Oxidative phosphorylation; Oxidative stress; Reactive oxygen species; Triphenylphosphonium cation.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Holmstrom K.M., Finkel T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014;15(6):411–421. - PubMed
-
- Galadari S., Rahman A., Pallichankandy S., Thayyullathil F. Reactive oxygen species and cancer paradox: to promote or to suppress? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017;104:144–164. - PubMed
-
- Winterbourn C.C. Reconciling the chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008;4(5):278–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

