Intermittent fasting protects against the deterioration of cognitive function, energy metabolism and dyslipidemia in Alzheimer's disease-induced estrogen deficient rats
- PMID: 29307281
- PMCID: PMC6022926
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370217751610
Intermittent fasting protects against the deterioration of cognitive function, energy metabolism and dyslipidemia in Alzheimer's disease-induced estrogen deficient rats
Abstract
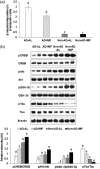
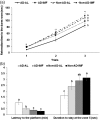
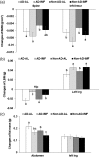
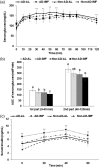
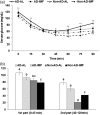
Intermittent fasting may be an effective intervention to protect against age-related metabolic disturbances, although it is still controversial. Here, we investigated the effect of intermittent fasting on the deterioration of the metabolism and cognitive functions in rats with estrogen deficiency and its mechanism was also explored. Ovariectomized rats were infused with β-amyloid (25-35; Alzheimer's disease) or β-amyloid (35-25, Non-Alzheimer's disease; normal cognitive function) into the hippocampus. Each group was randomly divided into two sub-groups: one with intermittent fasting and the other fed ad libitum: Alzheimer's disease-ad libitum, Alzheimer's disease-intermittent fasting, Non-Alzheimer's disease-ad libitum, and Non-Alzheimer's disease-intermittent fasting. Rats in the intermittent fasting groups had a restriction of food consumption to a 3-h period every day. Each group included 10 rats and all rats fed a high-fat diet for four weeks. Interestingly, Alzheimer's disease increased tail skin temperature more than Non-Alzheimer's disease and intermittent fasting prevented the increase. Alzheimer's disease reduced bone mineral density in the spine and femur compared to the Non-Alzheimer's disease, whereas bone mineral density in the hip and leg was reduced by intermittent fasting. Fat mass only in the abdomen was decreased by intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting decreased food intake without changing energy expenditure. Alzheimer's disease increased glucose oxidation, whereas intermittent fasting elevated fat oxidation as a fuel source. Alzheimer's disease and intermittent fasting deteriorated insulin resistance in the fasting state but intermittent fasting decreased serum glucose levels after oral glucose challenge by increasing insulin secretion. Alzheimer's disease deteriorated short and spatial memory function compared to the Non-Alzheimer's disease, whereas intermittent fasting prevented memory loss in comparison to ad libitum. Unexpectedly, cortisol levels were increased by Alzheimer's disease but decreased by intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting improved dyslipidemia and liver damage index compared to ad libitum. Alzheimer's disease lowered low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and serum triglyceride levels compared to Non-Alzheimer's disease. In conclusion, Alzheimer's disease impaired not only cognitive function but also disturbed energy, glucose, lipid, and bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats. Intermittent fasting protected against the deterioration of these metabolic parameters, but it exacerbated bone mineral density loss and insulin resistance at fasting in Alzheimer's disease-induced estrogen-deficient rats. Impact statement Intermittent fasting was evaluated for its effects on cognitive function and metabolic disturbances in a rat model of menopause and Alzheimer's disease. Intermittent fasting decreased skin temperature and fat mass, and improved glucose tolerance with decreasing food intake. Intermittent fasting also prevented memory loss: short-term and special memory loss. Therefore, intermittent fasting may prevent some of the metabolic pathologies associated with menopause and protect against age-related memory decline.
Keywords: Intermittent fasting; bone mineral density; dyslipidemia; glucose tolerance; insulin resistance; memory loss.
Figures
References
-
- Law J, Bloor I, Budge H, Symonds ME. The influence of sex steroids on adipose tissue growth and function. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 2014; 19:13–24 - PubMed
-
- Nedungadi TP, Clegg DJ. Sexual dimorphism in body fat distribution and risk for cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2009; 2:321–7 - PubMed
-
- Au A, Feher A, McPhee L, Jessa A, Oh S, Einstein G. Estrogens, inflammation and cognition. Front Neuroendocrinol 2016; 40:87–100 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

