Leptin Mediates a Glucose-Fatty Acid Cycle to Maintain Glucose Homeostasis in Starvation
- PMID: 29307489
- PMCID: PMC5766366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.001
Leptin Mediates a Glucose-Fatty Acid Cycle to Maintain Glucose Homeostasis in Starvation
Abstract
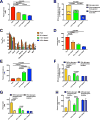
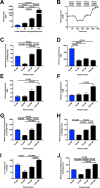
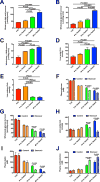
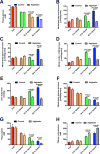
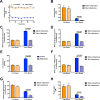
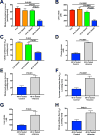
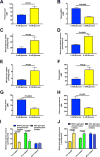
The transition from the fed to the fasted state necessitates a shift from carbohydrate to fat metabolism that is thought to be mostly orchestrated by reductions in plasma insulin concentrations. Here, we show in awake rats that insulinopenia per se does not cause this transition but that both hypoleptinemia and insulinopenia are necessary. Furthermore, we show that hypoleptinemia mediates a glucose-fatty acid cycle through activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, resulting in increased white adipose tissue (WAT) lipolysis rates and increased hepatic acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) content, which are essential to maintain gluconeogenesis during starvation. We also show that in prolonged starvation, substrate limitation due to reduced rates of glucose-alanine cycling lowers rates of hepatic mitochondrial anaplerosis, oxidation, and gluconeogenesis. Taken together, these data identify a leptin-mediated glucose-fatty acid cycle that integrates responses of the muscle, WAT, and liver to promote a shift from carbohydrate to fat oxidation and maintain glucose homeostasis during starvation.
Keywords: HPA axis; glucose-alanine cycling; leptin; starvation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Metabolism: Leptin's role in starvation.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Mar;14(3):129. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.6. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29348478 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature. 1996;382:250–252. - PubMed
-
- Benedict FG. A study of prolonged fasting. Carnegie Inst Wash Pub. 1907;77:66.
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian journal of biochemistry and physiology. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Cahill GF., Jr Starvation in man. The New England journal of medicine. 1970;282:668–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 DK101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087568/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA215315/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA215315/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

