The Dynamic Landscape of Open Chromatin during Human Cortical Neurogenesis
- PMID: 29307494
- PMCID: PMC5924568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.014
The Dynamic Landscape of Open Chromatin during Human Cortical Neurogenesis
Abstract
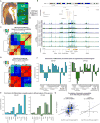
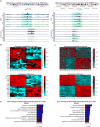
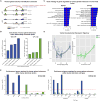
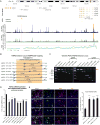
Non-coding regions comprise most of the human genome and harbor a significant fraction of risk alleles for neuropsychiatric diseases, yet their functions remain poorly defined. We created a high-resolution map of non-coding elements involved in human cortical neurogenesis by contrasting chromatin accessibility and gene expression in the germinal zone and cortical plate of the developing cerebral cortex. We link distal regulatory elements (DREs) to their cognate gene(s) together with chromatin interaction data and show that target genes of human-gained enhancers (HGEs) regulate cortical neurogenesis and are enriched in outer radial glia, a cell type linked to human cortical evolution. We experimentally validate the regulatory effects of predicted enhancers for FGFR2 and EOMES. We observe that common genetic variants associated with educational attainment, risk for neuropsychiatric disease, and intracranial volume are enriched within regulatory elements involved in cortical neurogenesis, demonstrating the importance of this early developmental process for adult human cognitive function.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; chromatin; enhancers; evolution; human neocortical development; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Weaving New Insights for the Genetic Regulation of Human Cognitive Phenotypes.Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):10-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.037. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29328907
-
Neural development: 'Enhancing' human cognition.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018 Mar;19(3):120-121. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.11. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29386613 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aarts E, Verhage M, Veenvliet JV, Dolan CV, van der Sluis S. A solution to dependency: using multilevel analysis to accommodate nested data. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:491–496. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Sagai T, Tanabe H, Mizushina Y, Nakazawa H, Shiroishi T. Chromosomal dynamics at the Shh locus: limb bud-specific differential regulation of competence and active transcription. Developmental cell. 2009;16:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Baala L, Briault S, Etchevers HC, Laumonnier F, Natiq A, Amiel J, Boddaert N, Picard C, Sbiti A, Asermouh A, et al. Homozygous silencing of T-box transcription factor EOMES leads to microcephaly with polymicrogyria and corpus callosum agenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39:454–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH103877/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103365/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH113823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110927/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HD035470/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103346/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103340/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103339/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH113823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH105881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH106934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM067553/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD087101/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105472/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH102357/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH102791/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

