Phlorizin Exerts Direct Protective Effects on Palmitic Acid (PA)-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway and Increasing the Levels of Nitric Oxide (NO)
- PMID: 29307883
- PMCID: PMC5771185
- DOI: 10.12659/msmbr.907775
Phlorizin Exerts Direct Protective Effects on Palmitic Acid (PA)-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway and Increasing the Levels of Nitric Oxide (NO)
Abstract
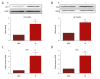
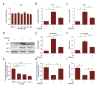
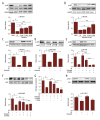
BACKGROUND Sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitors are the newest antidiabetic drugs that seem to be cardioprotective and can prevent type 2 diabetes in patients with high cardiovascular risks. Previous clinical trials have shown that these inhibitors can alleviate endothelial dysfunction, but the mechanism of action remains unknown. How SGLT inhibitor influences the release of NO in PA-induced HUVECs has never been reported. MATERIAL AND METHODS To explore the potential effects of the endothelial-protective mechanism of phlorizin and its impact on nitric oxide (NO), human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were incubated with palmitic acid (PA) and then treated with phlorizin. Western blotting was performed to assess the phosphorylation of AKT, eNOS, and IRS-1. To further explore potential targets, siRNA transfection was used to demonstrate the role of SGLT1 and SGLT2. RESULTS Phlorizin suppressed the expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2, activated the PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway, increased the output of NO, and promoted the consumption of glucose in PA-induced HUVECs. Through demonstrating siRNA suppression of the expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in PA-induced HUVECs, this study provides a new understanding of the mechanism behind SGLT1 and SGLT2. CONCLUSIONS Our data demonstrate that phlorizin ameliorates the endothelial dysfunction link with the activation of the PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway and augmentation of the release of NO, partially through suppressing the expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in PA-induced HUVECS.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lespedeza cuneata protects the endothelial dysfunction via eNOS phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in HUVECs.Phytomedicine. 2018 Sep 15;48:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 9. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30195866
-
Protective effects of 6-Gingerol on vascular endothelial cell injury induced by high glucose via activation of PI3K-AKT-eNOS pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:788-795. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.037. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28709132
-
Diosgenin ameliorates palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance via blocking IKKβ and IRS-1 pathways.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Aug;223(2):350-8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22766331
-
Mechanisms of Medicinal Plant Activity on Nitric Oxide (NO) Bioavailability as Prospective Treatments for Atherosclerosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(22):2591-2601. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200318152049. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32188375 Review.
-
Modulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase: a new cardiovascular therapeutic strategy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):H634-46. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01315.2010. Epub 2011 May 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21622818 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside.Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 25;11(5):389. doi: 10.3390/life11050389. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5634. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105634. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empagliflozin maintains capillarization and improves cardiac function in a murine model of left ventricular pressure overload.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 15;11(1):18384. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97787-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34526601 Free PMC article.
-
From Diabetes Care to Heart Failure Management: A Potential Therapeutic Approach Combining SGLT2 Inhibitors and Plant Extracts.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 10;14(18):3737. doi: 10.3390/nu14183737. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of endothelial progenitor cell microvesicles carrying miR‑98‑5p on angiotensin II‑induced rat kidney cell injury.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Sep 29;24(5):702. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11638. eCollection 2022 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36277153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ehrenkranz JR, Lewis NG, Kahn CR, et al. Phlorizin: A review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21(1):31–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

