Morin enhances hepatic Nrf2 expression in a liver fibrosis rat model
- PMID: 29307993
- PMCID: PMC5743504
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8334
Morin enhances hepatic Nrf2 expression in a liver fibrosis rat model
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether morin can reduce hepatic fibrosis by activating the NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway.
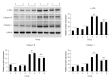
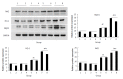
Methods: Twenty male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: control group, morin group, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) group, and morin + CCl4 group. Rats in both the CCl4 and morin + CCl4 groups were injected intraperitoneally with CCl4 at a dose of 2 mL/kg twice a week. Rats in both the morin and morin + CCl4 groups were treated orally with morin at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice a week. Control rats were treated with vehicle only twice a week. At the end-point of the 8 wk of the experimental period, serum AST, ALT, and ALP were measured, and the liver specimens were obtained for pathological assessment. Real-time PCR and Western blot methods were used to analyze the expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen I, collagen III, Nrf2, heme oxygenase (HO-1), and quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) using frozen liver specimens.
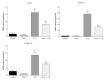
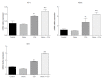
Results: Morin-treated rats in the morin + CCl4 group had less hyperplasia of fiber tissue, minimal inflammatory cells, and less body weight loss with favorable liver enzyme measurements compared to rats treated with CCl4 only. Additionally, morin-treated rats had significantly lower mRNA and protein expression of α-SMA, collagen I, and collagen III, but significantly higher mRNA and protein expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 compared to rats treated with CCl4 only (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Morin could play a protective role by inducing the expression of Nrf2 and its downstream antioxidant factors (HO-1 and NQO1) and reducing the expression of α-SMA, collagen I, and collagen III in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis rats.
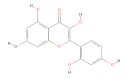
Keywords: Liver fibrosis; Morin; Nrf2; Rat.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of total flavonoids of Mallotus apelta (Lour.) Muell.Arg. leaf against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats via modulation of TGF-β1/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112714. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112714. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32105750
-
Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of Swertiamarin on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(6):2242-2254. doi: 10.1159/000475639. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28448964
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Is cirrhosis of the liver experimentally produced by CCl4 and adequate model of human cirrhosis?Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):112-20. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030118. Hepatology. 1983. PMID: 6337081 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nrf2 a molecular therapeutic target for Astaxanthin.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111374. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111374. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33761600 Review.
Cited by
-
[Morin Improves Experimental Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Rats via NLRP3/Caspase-1 Pathway].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Mar;52(2):229-234. doi: 10.12182/20210160507. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 33829696 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Acute aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic and cardiac oxidative damage in rats: Ameliorative effects of morin.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 4;9(11):e21837. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21837. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027731 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress Regarding the Effect and Mechanism of Dietary Polyphenols in Liver Fibrosis.Molecules. 2023 Dec 25;29(1):127. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010127. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Curcumin Alleviated Aflatoxin B1-Induced Acute Liver Damage in Ducks by Regulating NLRP3-Caspase-1 Signaling Pathways.Foods. 2021 Dec 13;10(12):3086. doi: 10.3390/foods10123086. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34945637 Free PMC article.
-
Morin as a Modulator of Hepatic Glucose Fluxes: A Balance Between Antihyperglycemic Potential and Mitochondrial Toxicity.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Jul;39(7):e70386. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70386. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40586287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simula MP, De Re V. Hepatitis C virus-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: a focus on recent advances in proteomics. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2010;4:782–793. - PubMed
-
- Clichici S, Catoi C, Mocan T, Filip A, Login C, Nagy A, Daicoviciu D, Decea N, Gherman C, Moldovan R, et al. Non-invasive oxidative stress markers for liver fibrosis development in the evolution of toxic hepatitis. Acta Physiol Hung. 2011;98:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Tipoe GL, Leung TM, Liong EC, Lau TY, Fung ML, Nanji AA. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces liver inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicology. 2010;273:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Lin PY, Chen CH, Wallace CG, Chen KH, Chang CL, Chen HH, Sung PH, Lin KC, Ko SF, Sun CK, et al. Therapeutic effect of rosuvastatin and propylthiouracil on ameliorating high-cholesterol diet-induced fatty liver disease, fibrosis and inflammation in rabbit. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9:3827–3841. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

