Improvements in Regional Left Ventricular Function Following Late Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Anterior Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 29308017
- PMCID: PMC5751905
- DOI: 10.1177/1179546817746636
Improvements in Regional Left Ventricular Function Following Late Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Anterior Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Late revascularization following a myocardial infarction has questionable clinical benefit.
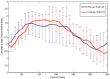
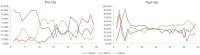
Methods: We studied 13 patients with anterior wall myocardial infarction who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention within 2 weeks of the primary event, by quantitative analysis of 2-dimensional echocardiographic images. Endocardial segmentations of the left ventricular (LV) endocardium from the 4-chamber views were studied over time to establish cumulative wall displacements (CWDs) throughout the cardiac cycle.
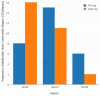
Results: Left ventricular end-systolic volume decreased to 42 ± 8 mL/body surface area (P = .034) and LV ejection fraction improved to 52% ± 7% (P = .04). Analysis of LV endocardial CWD demonstrated significant improvements in mid-systolic to late-systolic phases in the apical LV segments, from 3.5 ± 0.32 to 5.89 ± 0.43 mm (P = .019). Improvements in CWD were also observed in the late-diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle, from 1.50 ± 0.42 to 1.76 ± 0.52 mm (P = .04).
Conclusions: In our pilot patient cohort, following late establishment of infarct-related artery patency following an anterior wall myocardial infarction, regional improvements were noted in the LV apical segments during systole and late diastole.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction; infarct-related artery patency; percutaneous coronary intervention; revascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Steg G, James SK, Atar D, et al. ; Task Force Members. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2569–2619. - PubMed
-
- Wijns W, Kolh P, Danchin N, et al. ; Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS); European Association for Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2501–2555. - PubMed
-
- Horie H, Takahashi M, Minai K. Long-term beneficial effect of late reperfusion for acute anterior myocardial infarction with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation. 1998;98:2377–2382. - PubMed
-
- Yousef ZR, Redwood SR, Bucknall CA, Sulke AN, Marber MS. Late intervention after anterior myocardial infarction: effects on left ventricular size, function, quality of life, and exercise tolerance: results of the Open Artery Trial (TOAT study). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:869–876. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

