DOUBLY ROBUST ESTIMATION OF OPTIMAL TREATMENT REGIMES FOR SURVIVAL DATA-WITH APPLICATION TO AN HIV/AIDS STUDY
- PMID: 29308102
- PMCID: PMC5749433
- DOI: 10.1214/17-AOAS1057
DOUBLY ROBUST ESTIMATION OF OPTIMAL TREATMENT REGIMES FOR SURVIVAL DATA-WITH APPLICATION TO AN HIV/AIDS STUDY
Abstract
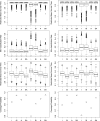
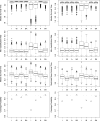
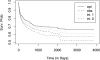
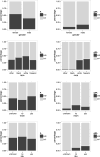
In many biomedical settings, assigning every patient the same treatment may not be optimal due to patient heterogeneity. Individualized treatment regimes have the potential to dramatically improve clinical outcomes. When the primary outcome is censored survival time, a main interest is to find optimal treatment regimes that maximize the survival probability of patients. Since the survival curve is a function of time, it is important to balance short-term and long-term benefit when assigning treatments. In this paper, we propose a doubly robust approach to estimate optimal treatment regimes that optimize a user specified function of the survival curve, including the restricted mean survival time and the median survival time. The empirical and asymptotic properties of the proposed method are investigated. The proposed method is applied to a data set from an ongoing HIV/AIDS clinical observational study conducted by the University of North Carolina (UNC) Center of AIDS Research (CFAR), and shows the proposed methods significantly improve the restricted mean time of the initial treatment duration. Finally, the proposed methods are extended to multi-stage studies.
Keywords: Doubly robust estimation; median survival time; optimal treatment regimen; restricted mean survival time.
Figures
References
-
- Chen PY, Tsiatis AA. Causal inference on the difference of the restricted mean lifetime between two groups. Biometrics. 2001;57:1030–1038. MR1950418. - PubMed
-
- Cox DR. Regression models and life-tables. J Roy Statist Soc Ser B. 1972;34:187–220. MR0341758.
-
- Dombrowski JC, Kitahata MM, Rompaey SEV, Crane HM, Mugavero MJ, Eron JJ, Boswell SL, Rodriguez B, Mathews WC, Martin JN, Moore RD, Golden MR. High levels of antiretroviral use and viral suppression among persons in HIV care in the United States, 2010. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013;63:299–306. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gill RD, Keiding N, Andersen PK. Statistical Models Based on Counting Processes. Springer; New York: 1997.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
