SALL4 as a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator in normal and leukemic hematopoiesis
- PMID: 29308206
- PMCID: PMC5751604
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-017-0115-6
SALL4 as a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator in normal and leukemic hematopoiesis
Abstract
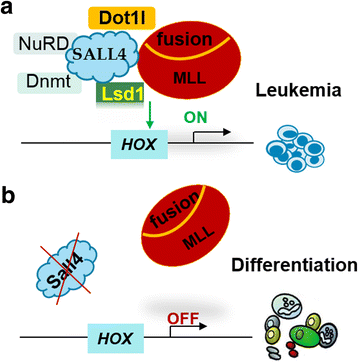
In recent years, there has been substantial progress in our knowledge of the molecular pathways by which stem cell factor SALL4 regulates the embryonic stem cell (ESC) properties, developmental events, and human cancers. This review summarizes recent advances in the biology of SALL4 with a focus on its regulatory functions in normal and leukemic hematopoiesis. In the normal hematopoietic system, expression of SALL4 is mainly enriched in the bone marrow hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSCs/HPCs), but is rapidly silenced following lineage differentiation. In hematopoietic malignancies, however, SALL4 expression is abnormally re-activated and linked with deteriorated disease status in patients. Further, SALL4 activation participates in the pathogenesis of tumor initiation and disease progression. Thus, a better understanding of SALL4's biologic functions and mechanisms will facilitate development of advanced targeted anti-leukemia approaches in future.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Chromatin modification; Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; Mixed-lineage leukemia; Pluripotency; Transgenic; Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The author declares that he has no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Kohlhase J, Schuh R, Dowe G, Kuhnlein RP, Jackle H, Schroeder B, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar HA, Kohler A, Muller U. Isolation, characterization, and organ-specific expression of two novel human zinc finger genes related to the drosophila gene spalt. Genomics. 1996;38 - PubMed
-
- Eildermann K, Aeckerle N, Debowski K, Godmann M, Christiansen H, Heistermann M, Schweyer S, Bergmann M, Kliesch S, Gromoll J, et al. Developmental expression of the pluripotency factor sal-like protein 4 in the monkey, human and mouse testis: restriction to premeiotic germ cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(3):206–220. doi: 10.1159/000335031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sweetman D, Munsterberg A. The vertebrate spalt genes in development and disease. Dev Biol. 2006;293(2):285–93. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Liao W, Ma Y. Role of SALL4 in hematopoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2012;19 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

