Changes in Inflammation but Not in T-Cell Activation Precede Non-AIDS-Defining Events in a Case-Control Study of Patients on Long-term Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 29309629
- PMCID: PMC6009591
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix666
Changes in Inflammation but Not in T-Cell Activation Precede Non-AIDS-Defining Events in a Case-Control Study of Patients on Long-term Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
Background: We examined changes in soluble inflammatory cytokines and T-cell activation after antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation in an AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG) nested case-control study.
Methods: Cases were 143 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected adults who developed a non-AIDS event; 315 controls remained event-free. Specimens were tested pre-ART, year 1 post-ART, and at the visit preceding the event. Conditional logistic regression evaluated the associations of biomarker changes with non-AIDS events.
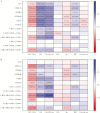
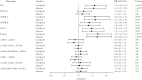
Results: Inflammatory and most activation biomarkers declined from pre-ART to year 1 for cases and controls. Subsequently, inflammatory biomarkers remained mostly stable in controls but not cases. Cellular activation markers generally declined for both cases and controls between year 1 and the pre-event sampling. Controls with greater pre-ART RNA levels or lower CD4+ levels had higher biomarker levels while also experiencing greater biomarker declines in the first year of ART. Changes in biomarkers to year 1 showed no significant associations with non-AIDS events. Cases, however, had significantly greater increases in all plasma biomarkers (but not cellular activation) from year 1 to the visit preceding the event.
Conclusions: Inflammation increases prior to non-AIDS events in treated HIV-infected adults. These biomarker changes may reflect subclinical disease processes or other alterations in the inflammatory environment that causally contribute to disease.
Clinical trials registration: NCT00001137.
Figures


References
-
- French MA, King MS, Tschampa JM, da Silva BA, Landay AL. Serum immune activation markers are persistently increased in patients with HIV infection after 6 years of antiretroviral therapy despite suppression of viral replication and reconstitution of CD4+ T cells. J Infect Dis 2009; 200:1212–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

