Posttranslational Modifications of RAS Proteins
- PMID: 29311131
- PMCID: PMC6035883
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a031484
Posttranslational Modifications of RAS Proteins
Abstract
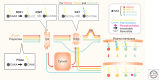
The three human RAS genes encode four proteins that play central roles in oncogenesis by acting as binary molecular switches that regulate signaling pathways for growth and differentiation. Each is subject to a set of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) that modify their activity or are required for membrane targeting. The enzymes that catalyze the various PTMs are potential targets for anti-RAS drug discovery. The PTMs of RAS proteins are the focus of this review.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmadian MR, Stege P, Scheffzek K, Wittinghofer A. 1997. Confirmation of the arginine-finger hypothesis for the GAP-stimulated GTP-hydrolysis reaction of Ras. Nat Struct Biol 4: 686–689. - PubMed
-
- Aktories K. 2011. Bacterial protein toxins that modify host regulatory GTPases. Nat Rev Microbiol 9: 487–498. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Moya B, Lopez-Alcala C, Drosten M, Bachs O, Agell N. 2010. K-Ras4B phosphorylation at Ser181 is inhibited by calmodulin and modulates K-Ras activity and function. Oncogene 29: 5911–5922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
