Troy+ brain stem cells cycle through quiescence and regulate their number by sensing niche occupancy
- PMID: 29311336
- PMCID: PMC5789932
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1715911114
Troy+ brain stem cells cycle through quiescence and regulate their number by sensing niche occupancy
Abstract
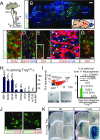
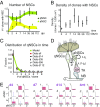
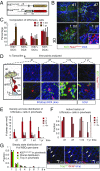
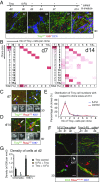
The adult mouse subependymal zone provides a niche for mammalian neural stem cells (NSCs). However, the molecular signature, self-renewal potential, and fate behavior of NSCs remain poorly defined. Here we propose a model in which the fate of active NSCs is coupled to the total number of neighboring NSCs in a shared niche. Using knock-in reporter alleles and single-cell RNA sequencing, we show that the Wnt target Tnfrsf19/Troy identifies both active and quiescent NSCs. Quantitative analysis of genetic lineage tracing of individual NSCs under homeostasis or in response to injury reveals rapid expansion of stem-cell number before some return to quiescence. This behavior is best explained by stochastic fate decisions, where stem-cell number within a shared niche fluctuates over time. Fate mapping proliferating cells using a Ki67iresCreER allele confirms that active NSCs reversibly return to quiescence, achieving long-term self-renewal. Our findings suggest a niche-based mechanism for the regulation of NSC fate and number.
Keywords: cellular dynamics; ki67; modeling; neural stem cells; single-cell sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- García-Verdugo JM, Doetsch F, Wichterle H, Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A. Architecture and cell types of the adult subventricular zone: In search of the stem cells. J Neurobiol. 1998;36:234–248. - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caillé I, Lim DA, García-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97:703–716. - PubMed
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to sonic hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

