Activation of a Cell Surface Signaling Pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Requires ClpP Protease and New Sigma Factor Synthesis
- PMID: 29312164
- PMCID: PMC5733041
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02442
Activation of a Cell Surface Signaling Pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Requires ClpP Protease and New Sigma Factor Synthesis
Abstract
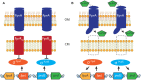
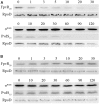
Extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors control expression of large numbers of genes in bacteria. Most ECF sigma factors are inhibited by antisigma proteins, with inhibition being relieved by environmental signals that lead to inactivation of the antisigma protein and consequent sigma factor activity. In cell surface signaling (CSS) systems in Gram negative bacteria antisigma activity is controlled by an outer membrane protein receptor and its ligand. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa one such system controls expression of genes for secretion and uptake of a siderophore, pyoverdine. In this system the activities of two sigma factors σFpvI and σPvdS are inhibited by antisigma protein FpvR20 that binds to the sigma factors, preventing their interaction with core RNA polymerase. Transport of ferripyoverdine by its outer membrane receptor FpvA causes proteolytic degradation of FpvR20, inducing expression of σFpvI- and σPvdS-dependent target genes. Here we show that degradation of FpvR20 and induction of target gene expression was initiated within 1 min of addition of pyoverdine. FpvR20 was only partially degraded in a mutant lacking the intracellular ClpP protease, resulting in an FpvR20 subfragment (FpvR12) that inhibited σFpvI and σPvdS. The translation inhibitor chloramphenicol did not prevent induction of an σFpvI-dependent gene, showing that degradation of FpvR20 released pre-existing σFpvI in an active form. However, chloramphenicol inhibited induction of σPvdS-dependent genes showing that active σPvdS is not released when FpvR20 is degraded and instead, σPvdS must be synthesized in the absence of FpvR20 to be active. These findings show that sigma factor activation occurs rapidly following addition of the inducing signal in a CSS pathway and requires ClpP protease. Induction of gene expression that can arise from release of active sigma from an antisigma protein but can also require new sigma factor synthesis.
Keywords: ClpP protease; ECF sigma factor; antisigma; bacterial signal transduction; cell surface signaling; pyoverdine; regulated proteolysis; siderophore.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The purification of the σFpvI/FpvR20 and σPvdS/FpvR20 protein complexes is facilitated at room temperature.Protein Expr Purif. 2019 Aug;160:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Protein Expr Purif. 2019. PMID: 30878602
-
Integrated activities of two alternative sigma factors coordinate iron acquisition and uptake by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Dec;106(6):891-904. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13855. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28971540
-
Interactions between an anti-sigma protein and two sigma factors that regulate the pyoverdine signaling pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Nov 30;14:287. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0287-2. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25433393 Free PMC article.
-
High affinity iron uptake by pyoverdine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involves multiple regulators besides Fur, PvdS, and FpvI.Biometals. 2023 Apr;36(2):255-261. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00369-6. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 35171432 Review.
-
Cell-surface signaling in Pseudomonas: stress responses, iron transport, and pathogenicity.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014 Jul;38(4):569-97. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12078. Epub 2014 Jul 2. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24923658 Review.
Cited by
-
The Burkholderia cenocepacia iron starvation σ factor, OrbS, possesses an on-board iron sensor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):3709-3726. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac137. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35234897 Free PMC article.
-
ClpP Protease, a Promising Antimicrobial Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 7;20(9):2232. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092232. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31067645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron Homeostasis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Targeting Iron Acquisition and Storage as an Antimicrobial Strategy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1386:29-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08491-1_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36258068
-
Plant-Derived Catechols Are Substrates of TonB-Dependent Transporters and Sensitize Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Siderophore-Drug Conjugates.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0149822. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01498-22. Epub 2022 Jun 30. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35770947 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of CspC Controls the Las Quorum-Sensing System through Translational Regulation of rsaL in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0054722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00547-22. Epub 2022 Apr 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35467416 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

