Engineering nanoparticles to overcome barriers to immunotherapy
- PMID: 29313006
- PMCID: PMC5689503
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10005
Engineering nanoparticles to overcome barriers to immunotherapy
Abstract
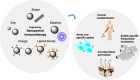
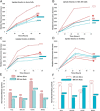
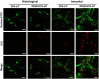
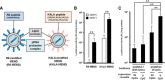
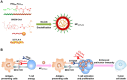
Advances in immunotherapy have led to the development of a variety of promising therapeutics, including small molecules, proteins and peptides, monoclonal antibodies, and cellular therapies. Despite this wealth of new therapeutics, the efficacy of immunotherapy has been limited by challenges in targeted delivery and controlled release, that is, spatial and temporal control on delivery. Particulate carriers, especially nanoparticles have been widely studied in drug delivery and vaccine research and are being increasingly investigated as vehicles to deliver immunotherapies. Nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery could provide several benefits, including control of biodistribution and transport kinetics, the potential for site-specific targeting, immunogenicity, tracking capability using medical imaging, and multitherapeutic loading. There are also a unique set of challenges, which include nonspecific uptake by phagocytic cells, off-target biodistribution, permeation through tissue (transport limitation), nonspecific immune-activation, and poor control over intracellular localization. This review highlights the importance of understanding the relationship between a nanoparticle's size, shape, charge, ligand density and elasticity to its vascular transport, biodistribution, cellular internalization, and immunogenicity. For the design of an effective immunotherapy, we highlight the importance of selecting a nanoparticle's physical characteristics (e.g., size, shape, elasticity) and its surface functionalization (e.g., chemical or polymer modifications, targeting or tissue-penetrating peptides) with consideration of its reactivity to the targeted microenvironment (e.g., targeted cell types, use of stimuli-sensitive biomaterials, immunogenicity). Applications of this rational nanoparticle design process in vaccine development and cancer immunotherapy are discussed.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; drug delivery; intracellular delivery; targeted nanoparticles; tissue permeation; vaccines.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JL, Smothers J, Srinivasan R, Hoos A. Big opportunities for small molecules in immuno‐oncology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(9):603–622. - PubMed
-
- Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(8):561–584. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

