Mutation update of transcription factor genes FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 causing cataracts and other developmental ocular defects
- PMID: 29314435
- PMCID: PMC5839989
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23395
Mutation update of transcription factor genes FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 causing cataracts and other developmental ocular defects
Abstract
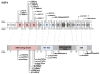
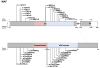
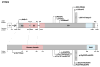
Mutations in the transcription factor genes FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 cause congenital lens defects including cataracts that may be accompanied by defects in other components of the eye or in nonocular tissues. We comprehensively describe here all the variants in FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 genes linked to human developmental defects. A total of 52 variants for FOXE3, 18 variants for HSF4, 20 variants for MAF, and 19 variants for PITX3 identified so far in isolated cases or within families are documented. This effort reveals FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 to have 33, 16, 18, and 7 unique causal mutations, respectively. Loss-of-function mutant animals for these genes have served to model the pathobiology of the associated human defects, and we discuss the currently known molecular function of these genes, particularly with emphasis on their role in ocular development. Finally, we make the detailed FOXE3, HSF4, MAF, and PITX3 variant information available in the Leiden Online Variation Database (LOVD) platform at https://www.LOVD.nl/FOXE3, https://www.LOVD.nl/HSF4, https://www.LOVD.nl/MAF, and https://www.LOVD.nl/PITX3. Thus, this article informs on key variants in transcription factor genes linked to cataract, aphakia, corneal opacity, glaucoma, microcornea, microphthalmia, anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis, and Ayme-Gripp syndrome, and facilitates their access through Web-based databases.
Keywords: Ayme-Gripp syndrome; LOVD; anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis; aphakia; cataract; microcornea.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Agrawal SA, Anand D, Siddam AD, Kakrana A, Dash S, Scheiblin DA, Dang CA, Terrell AM, Waters SM, Singh A, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M, et al. Compound mouse mutants of bZIP transcription factors Mafg and Mafk reveal a regulatory network of non-crystallin genes associated with cataract. Hum Genet. 2015;134:717–735. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad N, Aslam M, Muenster D, Horsch M, Khan MA, Carlsson P, Beckers J, Graw J. Pitx3 directly regulates Foxe3 during early lens development. Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57:741–751. - PubMed
-
- Aldahmesh MA, Khan AO, Mohamed J, Alkuraya FS. Novel recessive BFSP2 and PITX3 mutations: insights into mutational mechanisms from consanguineous populations. Genet Med Off J Am Coll Med Genet. 2011;13:978–981. - PubMed
-
- Ali M, Buentello-Volante B, McKibbin M, Rocha-Medina JA, Fernandez-Fuentes N, Koga-Nakamura W, Ashiq A, Khan K, Booth AP, Williams G, Raashid Y, Jafri H, et al. Homozygous FOXE3 mutations cause non-syndromic, bilateral, total sclerocornea, aphakia, microphthalmia and optic disc coloboma. Mol Vis. 2010;16:1162–1168. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

