Joint associations of a polygenic risk score and environmental risk factors for breast cancer in the Breast Cancer Association Consortium
- PMID: 29315403
- PMCID: PMC5913605
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyx242
Joint associations of a polygenic risk score and environmental risk factors for breast cancer in the Breast Cancer Association Consortium
Abstract
Background: Polygenic risk scores (PRS) for breast cancer can be used to stratify the population into groups at substantially different levels of risk. Combining PRS and environmental risk factors will improve risk prediction; however, integrating PRS into risk prediction models requires evaluation of their joint association with known environmental risk factors.
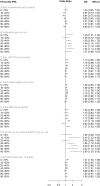
Methods: Analyses were based on data from 20 studies; datasets analysed ranged from 3453 to 23 104 invasive breast cancer cases and similar numbers of controls, depending on the analysed environmental risk factor. We evaluated joint associations of a 77-single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) PRS with reproductive history, alcohol consumption, menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), height and body mass index (BMI). We tested the null hypothesis of multiplicative joint associations for PRS and each of the environmental factors, and performed global and tail-based goodness-of-fit tests in logistic regression models. The outcomes were breast cancer overall and by estrogen receptor (ER) status.
Results: The strongest evidence for a non-multiplicative joint associations with the 77-SNP PRS was for alcohol consumption (P-interaction = 0.009), adult height (P-interaction = 0.025) and current use of combined MHT (P-interaction = 0.038) in ER-positive disease. Risk associations for these factors by percentiles of PRS did not follow a clear dose-response. In addition, global and tail-based goodness of fit tests showed little evidence for departures from a multiplicative risk model, with alcohol consumption showing the strongest evidence for ER-positive disease (P = 0.013 for global and 0.18 for tail-based tests).
Conclusions: The combined effects of the 77-SNP PRS and environmental risk factors for breast cancer are generally well described by a multiplicative model. Larger studies are required to confirm possible departures from the multiplicative model for individual risk factors, and assess models specific for ER-negative disease.
Figures
References
-
- Colditz GA, Baer HJ, Tamimi RM. Breast cancer. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF (eds). Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2006.
-
- Pharoah PD, Antoniou A, Bobrow M, Zimmern RL, Easton DF, Ponder BA. Polygenic susceptibility to breast cancer and implications for prevention. Nat Genet 2002;31:33–36. - PubMed
-
- Pharoah PD, Antoniou AC, Easton DF, Ponder BA. Polygenes, risk prediction, and targeted prevention of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2796–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA192393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical