Comparative effects of valsartan plus either cilnidipine or hydrochlorothiazide on home morning blood pressure surge evaluated by information and communication technology-based nocturnal home blood pressure monitoring
- PMID: 29316213
- PMCID: PMC8030821
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13154
Comparative effects of valsartan plus either cilnidipine or hydrochlorothiazide on home morning blood pressure surge evaluated by information and communication technology-based nocturnal home blood pressure monitoring
Abstract
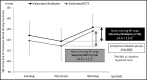
The authors tested the hypothesis that a valsartan/cilnidipine combination would suppress the home morning blood pressure (BP) surge (HMBPS) more effectively than a valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination in patients with morning hypertension, defined as systolic BP (SBP) ≥135 mm Hg or diastolic BP ≥85 mm Hg assessed by a self-measuring information and communication technology-based home BP monitoring device more than three times before either combination's administration. This was an 8-week prospective, multicenter, randomized, open-label clinical trial. The HMBPS, which is a new index, was defined as the mean morning SBP minus the mean nocturnal SBP, both measured on the same day. The authors randomly allocated 129 patients to the valsartan/cilnidipine (63 patients; mean 68.4 years) or valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide (66 patients; mean 67.3 years) combination groups, and the baseline HMBPS values were 17.4 mm Hg vs 16.9 mm Hg, respectively (P = .820). At the end of the treatment period, the changes in nocturnal SBP and morning SBP from baseline were significant in both the valsartan/cilnidipine and valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide groups (P < .001): -5.0 vs -10.0 mm Hg (P = .035) and -10.7 vs -13.6 mm Hg (P = .142), respectively. HMBPS was significantly decreased from baseline in both groups (P < .001), but there was no significant difference between the two groups: 14.4 mm Hg vs 14.0 mm Hg, respectively (P = .892). Valsartan/cilnidipine could not significantly suppress HMBPS compared with valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide. Large-scale randomized controlled studies are needed to assess how reducing HMBPS will affect future cardiovascular outcomes. The information and communication technology-based home BP monitoring device may become an alternative to ambulatory BP monitoring, which has been a gold standard to measure nocturnal BP and the morning BP surge.
Keywords: automatic information and communication technology-based home blood pressure monitoring device; home morning blood pressure surge; morning blood pressure; nocturnal blood pressure; valsartan/cilnidipine combination.
©2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative effects of valsartan plus cilnidipine or hydrochlorothiazide on nocturnal home blood pressure.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Mar;23(3):687-691. doi: 10.1111/jch.14199. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 33497537 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronotherapy with valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination in essential hypertension: improved sleep-time blood pressure control with bedtime dosing.Chronobiol Int. 2011 Aug;28(7):601-10. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2011.589935. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Chronobiol Int. 2011. PMID: 21823969 Clinical Trial.
-
Antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of two fixed-dose combinations of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide compared with valsartan monotherapy in patients with stage 2 or 3 systolic hypertension: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial.Clin Ther. 2005 Jul;27(7):1013-21. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.07.010. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16154480 Clinical Trial.
-
Research and Development of Information and Communication Technology-based Home Blood Pressure Monitoring from Morning to Nocturnal Hypertension.Ann Glob Health. 2016 Mar-Apr;82(2):254-73. doi: 10.1016/j.aogh.2016.02.004. Ann Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27372530 Review.
-
Valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide: a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic efficacy and place in the management of hypertension.Drugs. 2002;62(13):1983-2005. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262130-00015. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12215069 Review.
Cited by
-
Home Blood Pressure Monitoring: Current Status and New Developments.Am J Hypertens. 2021 Aug 9;34(8):783-794. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpab017. Am J Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 34431500 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of valsartan plus cilnidipine or hydrochlorothiazide on nocturnal home blood pressure.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Mar;23(3):687-691. doi: 10.1111/jch.14199. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 33497537 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of administration of low-dose irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide combined with levamlodipine at different times on the circadian rhythm of blood pressure and the levels of MMPs and TIMPs in non-dipper patients with grade 1 and 2 hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023 Feb;25(2):137-145. doi: 10.1111/jch.14630. Epub 2023 Jan 14. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023. PMID: 36639984 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Guidance on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: A statement from the HOPE Asia Network.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021 Mar;23(3):411-421. doi: 10.1111/jch.14128. Epub 2020 Dec 14. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021. PMID: 33319412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of different schedules of nocturnal home blood pressure measurement using an information/communication technology-based device in hypertensive patients.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018 Nov;20(11):1633-1641. doi: 10.1111/jch.13407. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018. PMID: 30350337 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I, et al. Home blood pressure measurement has a stronger predictive power for mortality than does screening blood pressure measurement: a population‐based observation in Ohasama, Japan. J Hypertens. 1998;16:971‐975. - PubMed
-
- Sega R, Facchetti R, Bombelli M, et al. Prognostic value of ambulatory and home blood pressures compared with office blood pressure in the general population: follow‐up results from the Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate e Loro Associazioni (PAMELA) study. Circulation. 2005;111:1777‐1783. - PubMed
-
- Stergiou GS, Baibas NM, Kalogeropoulos PG. Cardiovascular risk prediction based on home blood pressure measurement: the Didima study. J Hypertens. 2007;25:1590‐1596. - PubMed
-
- Niiranen TJ, Hanninen MR, Johansson J, Reunanen A, Jula AM. Home‐measured blood pressure is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular risk than office blood pressure: the Finn‐Home study. Hypertension. 2010;55:1346‐1351. - PubMed
-
- Gosse P, Ansoborio P, Lemetayer P, Clementy J. Left ventricular mass is better correlated with arising blood pressure than with office or occasional blood pressure. Am J Hypertens. 1997;10:505‐510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

