Solid-Phase Synthesis of β-Amino Ketones Via DNA-Compatible Organocatalytic Mannich Reactions
- PMID: 29316387
- PMCID: PMC7074847
- DOI: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00151
Solid-Phase Synthesis of β-Amino Ketones Via DNA-Compatible Organocatalytic Mannich Reactions
Abstract
One-bead-one-compound (OBOC) libraries constructed by solid-phase split-and-pool synthesis are a valuable source of protein ligands. Most OBOC libraries are comprised of oligoamides, particularly peptides, peptoids, and peptoid-inspired molecules. Further diversification of the chemical space covered by OBOC libraries is desirable. Toward this end, we report here the efficient proline-catalyzed asymmetric Mannich reaction between immobilized aldehydes and soluble ketones and anilines. The reaction conditions do not compromise the amplification of DNA by the PCR. Thus, this chemistry will likely be useful for the construction of novel DNA-encoded libraries by solid-phase synthesis.
Keywords: DNA-encoded libraries; Mannich reaction; one-bead-one-compound libraries; organocatalysis; solid-phase synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
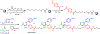
References
-
- Houghten RA; Pinilla C; Blondelle SE; Appel JR; Dooley CT; Cuervo JH Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature 1991, 354 (6348), 84–6. - PubMed
-
- Hoesl CE; Nefzi A; Ostresh JM; Yu Y; Houghten RA Mixture-based combinatorial libraries: from peptides and peptidomi-metics to small molecule acyclic and heterocyclic compounds. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 369, 496–517. - PubMed
-
- Fleeman R; LaVoi TM; Santos RG; Morales A; Nefzi A; Welmaker GS; Medina-Franco JL; Giulianotti MA; Houghten RA; Shaw LN Combinatorial Libraries As a Tool for the Discovery of Novel, Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Agents Targeting the ESKAPE Pathogens. J. Med. Chem 2015, 58 (8), 3340–55. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lam KS; Salmon SE; Hersh EM; Hruby VJ; Kazmierski WM; Knapp RJ A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature 1991, 354, 82–84. - PubMed
-
- Alluri PG; Reddy MM; Bachhawat-Sikder K; Olivos HJ; Kodadek T. Isolation of protein ligands from large peptoid libraries. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125 (46), 13995–4004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

