Liposomal Delivery of Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental Tissue Regeneration
- PMID: 29316874
- PMCID: PMC6033301
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2017.0419
Liposomal Delivery of Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
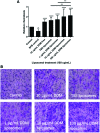
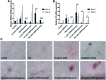
Current dental restorations have short longevity, and consequently, there is a need for novel tissue engineering strategies that aim to regenerate the dentin-pulp complex. Dentin matrix contains a myriad of bioactive growth factors and extracellular matrix proteins associated with the recruitment, proliferation, and differentiation of dental pulp progenitor cells. In this study, we show that demineralized dentin matrix (DDM), from noncarious dentine, can be encapsulated into liposomes for delivery to dental tissue to promote regeneration. Liposomes were formulated to encapsulate 0-100 μg/mL DDM, lysed with Triton X, and used in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to quantify release. The encapsulation efficiencies were calculated to be 25.9% and 28.8% (VEGF/TGF-β1) for 50 μg/mL DDM liposomes and 39% and 146.7% (VEGF/TGF-β1) for 100 μg/mL DDM liposomes. All liposome formulations had no cytotoxic effects on a dental pulp stem cell (DPSC) clone, as shown by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltertrazolium bromide), Caspase 3/7 assays, and cell counts. The ability of the liposomes to stimulate DPSC chemotactic recruitment was tested by Boyden chamber chemotaxis assays. Unloaded liposomes alone stimulated significant progenitor cell recruitment, while DDM-loaded liposomes further promoted chemotactic recruitment in a dose-dependent manner. DDM liposomes promoted the upregulation of "osteodentin" markers osteocalcin and RUNX2 (Runt-related transcription factor 2) in DPSCs after 9 days of treatment, determined by real-time quantitative PCR. Furthermore, Alizarin Red S staining showed that unloaded liposomes alone induced biomineralization of DPSCs, and DDM liposomes further increased the amount of mineralization observed. DDM liposomes were more effective than free DDM (10 μg/mL) at activating recruitment and osteogenic differentiation of DPSC, which are key events in the endogenous repair of the dentin-pulp complex. The study has highlighted the therapeutic potential of bioactive DDM liposomes in activating dental tissue repair in vitro, suggesting that liposomal delivery from biomaterials could be a valuable tool for reparative dentistry and hard-tissue engineering applications.
Keywords: demineralized dentin matrix; dental pulp stem cells; dental tissue engineering; liposomes; odontogenesis; reparative dentinogenesis; restorative materials.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Sloan A.J., and Smith A.J. Stem cells and the dental pulp: potential roles in dentine regeneration and repair. Oral Dis 2, 151, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Tziafas D. Mechanisms controlling secondary initiation of dentinogenesis. Int Endod J 27, 61, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Smith A.J., Scheven B.A., Takahashi Y., Ferracane J.L., Shelton R.M., and Cooper P.R. Dentine as a bioactive extracellular matrix. Arch Oral Biol 57, 109, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Chun S.Y., Lee H.J., Choi Y.A., et al. . Analysis of the soluble human tooth proteome and its ability to induce dentin/tooth regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A 17, 181, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Bègue-Kirn C., Smith A., Ruch J., et al. . Effects of dentin proteins, transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF beta 1) and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) on the differentiation of odontoblast in vitro. Int J Dev Biol 36, 491, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
