Efficacy and safety of curcumin and its combination with boswellic acid in osteoarthritis: a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 29316908
- PMCID: PMC5761198
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-2062-z
Efficacy and safety of curcumin and its combination with boswellic acid in osteoarthritis: a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this clinical trial was to assess the efficacy and safety of curcuminoid complex extract from turmeric rhizome with turmeric volatile oil (CuraMed®) and its combination with boswellic acid extract from Indian frankincense root (Curamin®) vs placebo for the treatment of 40- to 70-year-old patients with osteoarthritis (OA).
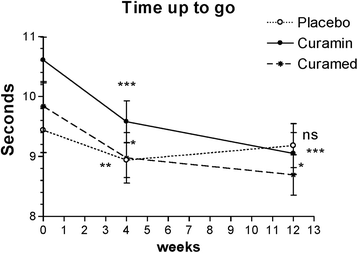
Methods: The effects of CuraMed® 500-mg capsules (333 mg curcuminoids) and Curamin® 500-mg capsules (350 mg curcuminoids and 150 mg boswellic acid) taken orally three times a day for 12 weeks in 201 patients was investigated in a three-arm, parallel-group, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Primary outcome efficacy measures included OA physical function performance-based tests, the WOMAC recommended index of joint pain, morning stiffness, limitations of physical function, and the patients' global assessment of disease severity.
Results: Favorable effects of both preparations compared to placebo were observed after only 3 months of continuous treatment. A significant effect of Curamin® compared to placebo was observed both in physical performance tests and the WOMAC joint pain index, while superior efficacy of CuraMed vs placebo was observed only in physical performance tests. The effect size compared to placebo was comparable for both treatment groups but was superior in the Curamin® group. The treatments were well tolerated.
Conclusions: Twelve-week use of curcumin complex or its combination with boswellic acid reduces pain-related symptoms in patients with OA. Curcumin in combination with boswellic acid is more effective. Combining Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts in Curamin® increases the efficacy of OA treatment presumably due to synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acid.
Trial registration: This trial is registered at the database www.clinicaltrials.gov . https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02390349?term=EuroPharma&rank=1 . Study registration number: NCT02390349 .
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the local Ethics Committee (Health Research Ethics Board at the Yerevan Medical State University of Armenia; 96/13; 22.04.2013), which approved all procedures and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and local laws and regulations. All participants gave written informed consent. Approved all procedures and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Verum and placebo capsules used in the study were donated by the manufacturer Europharma USA Inc. Europharma USA Inc. had no other involvement in the study.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bio-optimized Curcuma longa extract is efficient on knee osteoarthritis pain: a double-blind multicenter randomized placebo controlled three-arm study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jul 27;21(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1960-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31351488 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A standardized Boswellia serrata extract shows improvements in knee osteoarthritis within five days-a double-blind, randomized, three-arm, parallel-group, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1428440. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428440. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39092235 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a novel Boswellia serrata extract in the management of osteoarthritis of the knee.Phytother Res. 2019 May;33(5):1457-1468. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6338. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30838706 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of Curcuma longa extract and curcumin supplements on osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jun 25;41(6):BSR20210817. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210817. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34017975 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of curcumin and Boswellia for knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018 Dec;48(3):416-429. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018. PMID: 29622343 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jul 17;20(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02985-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32680575 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin-Based Fixed Dose Combination Products for Cholesterol Management: A Narrative Review.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jan 9;7(2):300-308. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00234. eCollection 2024 Feb 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38357288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological effects, formulations, and clinical research progress of curcumin.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1509045. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1509045. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40166470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Delivery Strategies and Nanozyme Technologies to Overcome Limitations for Targeting Oxidative Stress in Osteoarthritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jul 23;16(7):1044. doi: 10.3390/ph16071044. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37513955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of curcuminoids alone in alleviating pain and dysfunction for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Oct 19;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03740-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36261810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakagawa Y, Mukai S, Yamada S, Matsuoka M, Tarumi E, Hashimoto T, Tamura C, Imaizumi A, Nishihira J, Nakamura T. Short-term effects of highly-bioavailable curcumin for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled prospective study. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19:933–939. doi: 10.1007/s00776-014-0633-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Dugall M, Pellegrini L, Ledda A, Grossi MG, Togni S, Appendino G. Efficacy and safety of Meriva®, a curcumin-phosphatidylcholine complex, during extended administration in osteoarthritis patients. Altern Med Rev. 2010;15:337–344. - PubMed
-
- Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Dugall M, Pellegrini L, Ledda A, Grossi MG, Togni S, Appendino G. Product-evaluation registry of Meriva®, a curcumin-phosphatidylcholine complex, for the complementary management of osteoarthritis. Panminerva Med. 2010;52:55–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

