Gamma-delta (γδ) T cells: friend or foe in cancer development?
- PMID: 29316940
- PMCID: PMC5761189
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1378-2
Gamma-delta (γδ) T cells: friend or foe in cancer development?
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Gamma-delta (γδ) T cells: friend or foe in cancer development?J Transl Med. 2018 May 8;16(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1491-x. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29739416 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: γδ T cells are a distinct subgroup of T cells containing T cell receptors (TCRs) γ and TCR δ chains with diverse structural and functional heterogeneity. As a bridge between the innate and adaptive immune systems, γδ T cells participate in various immune responses during cancer progression. Because of their direct/indirect antitumor cytotoxicity and strong cytokine production ability, the use of γδ T cells in cancer immunotherapy has received a lot of attention over the past decade.
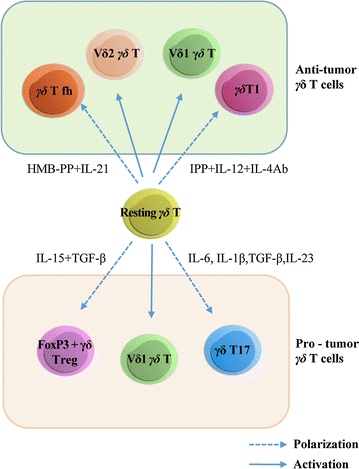
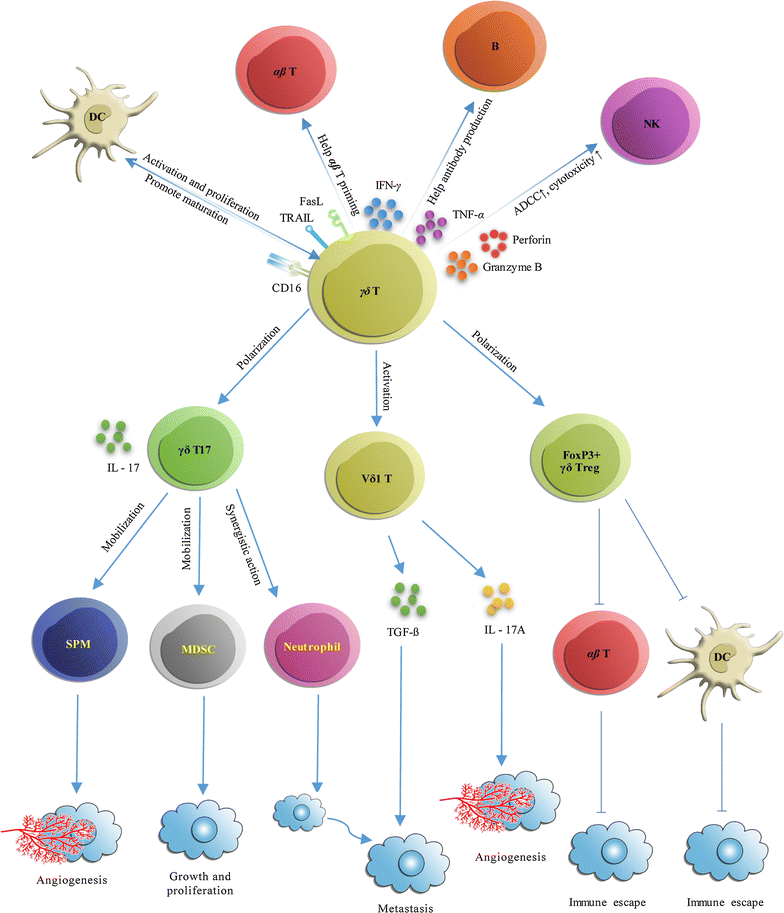
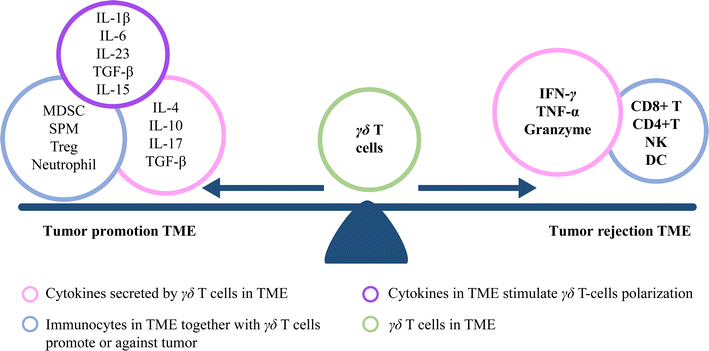
Main text: Despite the promising potential of γδ T cells, the efficacy of γδ T cell immunotherapy is limited, with an average response ratio of only 21%. In addition, research over the past 2 years has shown that γδ T cells could also promote cancer progression by inhibiting antitumor responses, and enhancing cancer angiogenesis. As a result, γδ T cells have a dual effect and can therefore be considered as being both "friends" and "foes" of cancer. In order to solve the sub-optimal efficiency problem of γδ T cell immunotherapy, we review recent observations regarding the antitumor and protumor activities of major structural and functional subsets of human γδ T cells, describing how these subsets are activated and polarized, and how these events relate to subsequent effects in cancer immunity. A mixture of both antitumor or protumor γδ T cells used in adoptive immunotherapy, coupled with the fact that γδ T cells can be polarized from antitumor cells to protumor cells appear to be the likely reasons for the mild efficacy seen with γδ T cells.
Conclusion: The future holds the promise of depleting the specific protumor γδ T cell subgroup before therapy, choosing multi-immunocyte adoptive therapy, modifying the cytokine balance in the cancer microenvironment, and using a combination of γδ T cells adoptive immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: Adoptive immunotherapy; Antitumor; Cytokine; Polarization; Protumor; Tumor microenvironment; γδ T cells.
Figures
References
-
- Holtmeier W, Kabelitz D. γδ T cells link innate and adaptive immune responses. In: Kabelitz D, Schröder JM, editors. Mechanisms of epithelial defense. Basel: Karger Publishers; 2005. pp. 151–183.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 816722751004388/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2016YFC1303800/National Key research and Development Program of China/International
- 20170622011JC/Key Laboratory Construction Project of Science and Technology Department/International
- 2017C022/the Industrial Research and Development Project of Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province/International
- 2014N147/the Project of Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

