Progress in antischistosomal N,N'-diaryl urea SAR
- PMID: 29317164
- PMCID: PMC6026081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.12.064
Progress in antischistosomal N,N'-diaryl urea SAR
Abstract
N,N'-Diaryl ureas have recently emerged as a new antischistosomal chemotype. We now describe physicochemical profiling, in vitro ADME, plasma exposure, and ex vivo and in vivo activities against Schistosoma mansoni for twenty new N,N'-diaryl ureas designed primarily to increase aqueous solubility, but also to maximize structural diversity. Replacement of one of the 4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl substructures of lead N,N'-diaryl urea 1 with azaheterocycles and benzoic acids, benzamides, or benzonitriles decreased lipophilicity, and in most cases, increased aqueous solubility. There was no clear relationship between lipophilicity and metabolic stability, although all compounds with 3-trifluoromethyl-4-pyridyl substructures were metabolically stable. N,N'-diaryl ureas containing 4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 3-trifluoromethyl-4-pyridyl, 2,2-difluorobenzodioxole, or 4-benzonitrile substructures had high activity against ex vivo S. mansoni and relatively low cytotoxicity. N,N-diaryl ureas with 3-trifluoromethyl-4-pyridyl and 2,2-difluorobenzodioxole substructures had the highest exposures whereas those with 4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl substructures had the best in vivo antischistosomal activities. There was no direct correlation between compound exposure and in vivo activity.
Keywords: Antischistosomal; N,N′-Diaryl urea; SAR.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
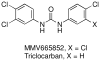

References
-
- Gryseels B. Schistosomiasis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012;26:383–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

