Adult-Type Rhabdomyoma of the Larynx: Clinicopathologic Study of an Uncommon Tumor in a Rare Location
- PMID: 29318074
- PMCID: PMC5727691
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7186768
Adult-Type Rhabdomyoma of the Larynx: Clinicopathologic Study of an Uncommon Tumor in a Rare Location
Abstract
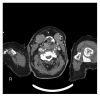
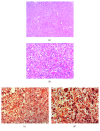
Rhabdomyoma is an uncommon benign mesenchymal tumor with skeletal muscle differentiation that may occur either in the heart or in extracardiac sites. Even though the head and neck region is the most common area of extracardiac rhabdomyoma, the larynx is rarely involved. We present the case of an 85-year-old woman who reported a 10-day history of breathing difficulties, dysphagia, and dysphonia. A computed tomography scan of the head and neck showed a contrast-enhanced, solid hypopharyngeal-laryngeal neoplasm with well-defined margins causing subtotal obliteration of the right pyriform sinus and a reduction in air lumen of the laryngeal vestibule. The patient underwent complete endoscopic removal of the lesion; histologic examination revealed an adult-type rhabdomyoma based on the histologic features and the immunoreactivity of the neoplastic cells for desmin, myoglobin, and muscle-specific actin but not for cytokeratin, S-100, CD68R, chromogranin-A, and synaptophysin. Since clinical and imaging features are not specific for rhabdomyoma, histologic examination and immunohistochemical analyses play a central role in the differential diagnosis of the adult-type rhabdomyoma from other laryngeal neoplasms. A correct diagnosis is mandatory to avoid inappropriate treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Goldblum J. R., Weiss S. W., Folpe A. L. Enzinger and Weiss’s Soft Tissue Tumors. Chapter 19: Rhabdomyoma. 6th. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013. pp. 591–600.
-
- Gorlin R. J. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Dermatologic Clinics. 1995;13(1):113–125. - PubMed
-
- Tostar U., Malm C. J., Meis-Kindblom J. M., Kindblom L. G., Toftgärd R., Undén A. B. Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: a possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. Journal of Pathology. 2006;208(1):17–25. doi: 10.1002/path.1882. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

