Anticancer Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 29318217
- PMCID: PMC5720534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.02.008
Anticancer Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
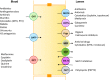
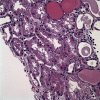
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a growing problem with untoward economic and medical consequences. Anticancer drug toxicity remains an important and increasing cause of AKI. Importantly, drug-induced AKI affects all nephron segments-vasculature, glomerulus, tubules, and interstitium. Recent studies have increased insight into the subcellular mechanisms of drug-induced AKI that include direct cellular toxicity and immune-mediated effects. Identification of patients with high-risk cancer before drug exposure may allow prevention or at least a reduction in the development and severity of nephrotoxicity. Recognition of drug-induced AKI and rapid discontinuation (or dose reduction) of the offending agents, when appropriate, are critical to maximizing kidney function recovery. Preventive measures require understanding patient and drug-related risk factors coupled with correcting risk factors, assessing baseline kidney function before initiation of therapy, adjusting the drug dosage and avoiding use of nephrotoxic drug combinations.
Keywords: acute interstitial nephritis; acute kidney injury; acute tubular necrosis; drug nephrotoxicity; glomerulopathy; onco-nephrology; thrombotic microangiopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Koyner J.L., Cerdá J., Goldstein S.L. Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group of the American Society of Nephrology. The daily burden of acute kidney injury: a survey of U.S. nephrologists on World Kidney Day. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Perazella M.A. Renal vulnerability to drug toxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4:1275–1283. - PubMed
-
- Kane-Gill S.L., Goldstein S.L. Drug-induced acute kidney injury: a focus on risk assessment for prevention. Crit Care Clin. 2015;31:675–684. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

