Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 29319049
- PMCID: PMC5765236
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.434
Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
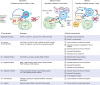
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) targeting CTLA-4 and the PD-1/PD-L1 axis have shown unprecedented clinical activity in several types of cancer and are rapidly transforming the practice of medical oncology. Whereas cytotoxic chemotherapy and small molecule inhibitors ('targeted therapies') largely act on cancer cells directly, immune checkpoint inhibitors reinvigorate anti-tumour immune responses by disrupting co-inhibitory T-cell signalling. While resistance routinely develops in patients treated with conventional cancer therapies and targeted therapies, durable responses suggestive of long-lasting immunologic memory are commonly seen in large subsets of patients treated with ICI. However, initial response appears to be a binary event, with most non-responders to single-agent ICI therapy progressing at a rate consistent with the natural history of disease. In addition, late relapses are now emerging with longer follow-up of clinical trial populations, suggesting the emergence of acquired resistance. As robust biomarkers to predict clinical response and/or resistance remain elusive, the mechanisms underlying innate (primary) and acquired (secondary) resistance are largely inferred from pre-clinical studies and correlative clinical data. Improved understanding of molecular and immunologic mechanisms of ICI response (and resistance) may not only identify novel predictive and/or prognostic biomarkers, but also ultimately guide optimal combination/sequencing of ICI therapy in the clinic. Here we review the emerging clinical and pre-clinical data identifying novel mechanisms of innate and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Anagnostou V, Smith KN, Forde PM, Niknafs N, Bhattacharya R, White J, Zhang T, Adleff V, Phallen J, Wali N, Hruban C, Guthrie VB, Rodgers K, Naidoo J, Kang H, Sharfman W, Georgiades C, Verde F, Illei P, Li QK, Gabrielson E, Brock MV, Zahnow CA, Baylin SB, Scharpf RB, Brahmer JR, Karchin R, Pardoll DM, Velculescu VE (2016) Evolution of neoantigen landscape during immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov 7(3): 264–276. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry D, Freeman GJ, Rodig SJ, Chapuy B, Ligon AH, Zhu L, Grosso JF, Kim SY, Timmerman JM, Shipp MA, Armand P (2015) PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 372(4): 311–319. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arlauckas SP, Garris CS, Kohler RH, Kitaoka M, Cuccarese MF, Yang KS, Miller MA, Carlson JC, Freeman GJ, Anthony RM, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2017) In vivo imaging reveals a tumour-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy. Sci Transl Med; e-pub ahead of print 10 May 2017; doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benci JL, Xu B, Qiu Y, Wu TJ, Dada H, Twyman-Saint Victor C, Cucolo L, Lee DS, Pauken KE, Huang AC, Gangadhar TC, Amaravadi RK, Schuchter LM, Feldman MD, Ishwaran H, Vonderheide RH, Maity A, Wherry EJ, Minn AJ (2016) Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 167(6): 1540–1554 e12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

